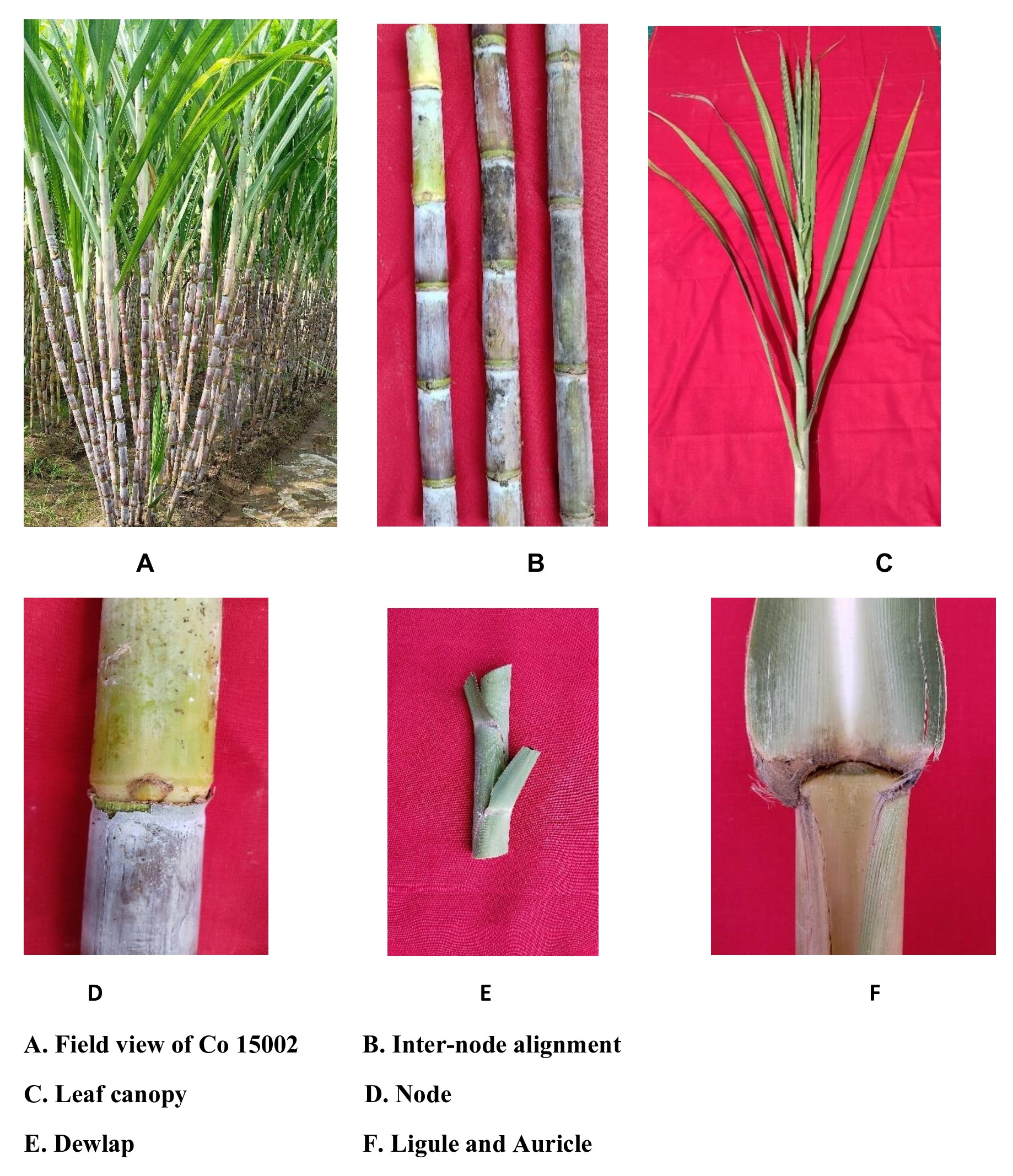
Recent Research Achievements
Crop Improvement
Crop Production
Crop Protection
Agricultural extension
Statistics and Economics
Division of Crop Improvement
Targeted improvement of stress tolerance, nutritional quality and yield of crops using Genome Editing in Sugarcane
Editing of the MATL gene by CRISPR-Cas for haploid induction in sugarcane
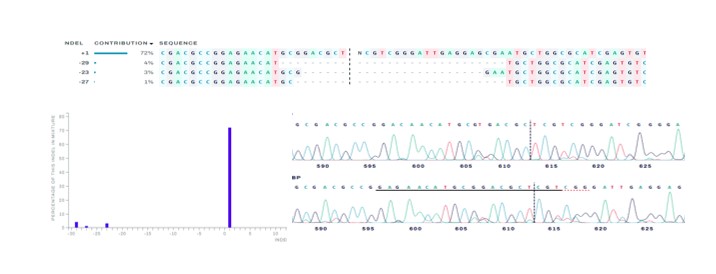
The poly cistronic tRNA gRNA method was optimized to edit the matrilineal (MATL) gene in sugarcane using three CRISPR-based DNA constructs. Guide RNAs with high cutting efficiency were selected and combined into a single editing system. The constructs were first tested and then transferred into sugarcane. More than 300 transformed plants were screened using DNA-based tests, and two plants were finally confirmed to carry the desired gene edits.

Fig G) Indels detected in the mutants generated with matl gene
Inputs from Dr R. Manimekalai, V.P. Sobhakumari and C. Appunu
Breeding
Variety Development
Four superior sugarcane varieties released and notified by CVRC/SVRC during 2022–2024:
Co 14012 (Avani)
- Type: Mid-late maturing sugarcane variety
- Developed by: ICAR–Sugarcane Breeding Institute (ICAR–SBI), Coimbatore
- Released through: Central Varietal Release Committee (CVRC), 2022
- Zone: Peninsular Zone
- Recommended States: Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Interior Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Karnataka, Gujarat, Maharashtra, and Madhya Pradesh
Performance:
- Parentage: Co 86032 x Co 86011
- Cane yield – 109.82 t/ha
- CCS yield – 16.16 t/ha
- Juice sucrose – 20.63%
Disease reaction:
- Red rot: Resistant (Nodal method), Moderately resistant (plug method)
- Smut: Resistant
- Yellow Leaf Disease (YLD): Resistant

Co 14005 (Arunima)
- Type: Mid-late maturing sugarcane variety
- Developed by: ICAR–Sugarcane Breeding Institute (ICAR–SBI), Coimbatore
- Released through: Central Varietal Release Committee (CVRC), 2023
- Zone: Peninsular Zone
- Recommended States: Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Interior Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Karnataka, Gujarat, Maharashtra, and Madhya Pradesh
Performance
- Parentage: Co 86032 x Co 86011
- Cane yield – 118.77 t/ha
- Sugar yield – 16.61 t/ha
- Juice sucrose – 20.15 %
Salient Features
- Resistant to red rot, smut and YLD
- Shows superior performance in waterlogged conditions (Kolhapur region)
- Less susceptible to major insect pests

Co 11015 (Atulya)
- Type: Early maturing variety
- Developed by: ICAR–Sugarcane Breeding Institute (ICAR–SBI), Coimbatore
- Released through: Central Varietal Release Committee (CVRC), 2022
- Zone: Peninsular Zone
- Recommended States: Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Interior Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Karnataka, Gujarat, Maharashtra, and Madhya Pradesh
- Suitable for: 8–12 months harvest and special season planting
Performance
- Parentage: CoC 671 x Co 86011
- Cane yield – 108.30 t/ha
- CCS yield – 16.22 t/ha
- Juice sucrose –21. 33 %
Disease Reaction
- Red rot – Resistant (Nodal)
- Smut – Resistant
- Wilt – Resistant
- YLD – Resistant
Special Traits
- High sucrose accumulation at 240, 300 and 360 days
- Excellent ratooning ability

Co 18009 (Punnakai)
- Type: Mid-late maturing variety
- Released through: SVRC (2023) – for Tamil Nadu (irrigated conditions)
- Parentage: Co 07027 × ISH 69
Performance
- Cane yield –153.85 t/ha
- Yield advantage – ≈ 10.85 % over Co 86032
Salient Features
- Good ratooner and drought tolerant
- Moderately resistant to red rot
- Suitable for machine harvesting
- Less susceptible to shoot and internode borers

iii New Sugarcane Clone identified through AICRP(S) (2023-25) for Peninsular India
Co 18003
- Co 18003 is a high-quality sugarcane clone suitable for cultivation in peninsular zone comprising states of Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Karnataka, Kerala, Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Tamil Nadu and Telangana.
- This clone recorded sugar yield of 16.58 t/ha at 360 days across the peninsular zone with an overall improvement of 14.96 %, 9.76 % and 4.20 % over the standards CoC 671 (14.42 t/ha), Co 09004 (15.10 t/ha) and Co 86032 (15.91 t/ha) respectively.
- Co 18003 recorded cane yield of 116.98 t/ha and registered an improvement of 17.31 %, 11.23 % and 0.91 % in comparison with the standards CoC 671 (99.73 t/ha), Co 09004 (105.17 t/ha) and Co 86032 (115.93 t/ha)
- Co 18003 registered its superiority for sugar yield and juice sucrose % by surpassing all three zonal standards (Co 86032, CoC 671, Co 09004) and emerged as only qualifying entry in 40 trials conducted across the zone.
- Co 18003 is R-MR (Resistant to moderately resistant) for red rot and resistant to Pokkah Boeng and Yellow leaf disease (YLD)
- This clone is less susceptible to top borer and scale insect in all the locations tested. It was less susceptible to moderately susceptible for early shoot borer and internode borer.

Breeding Sugarcane for High Biomass Production
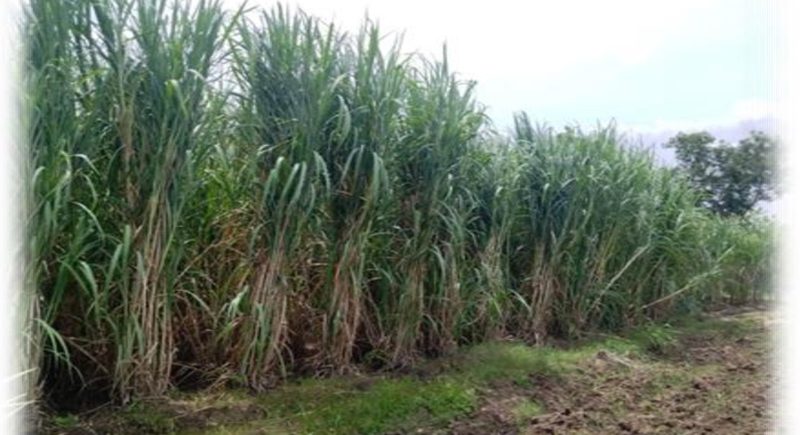
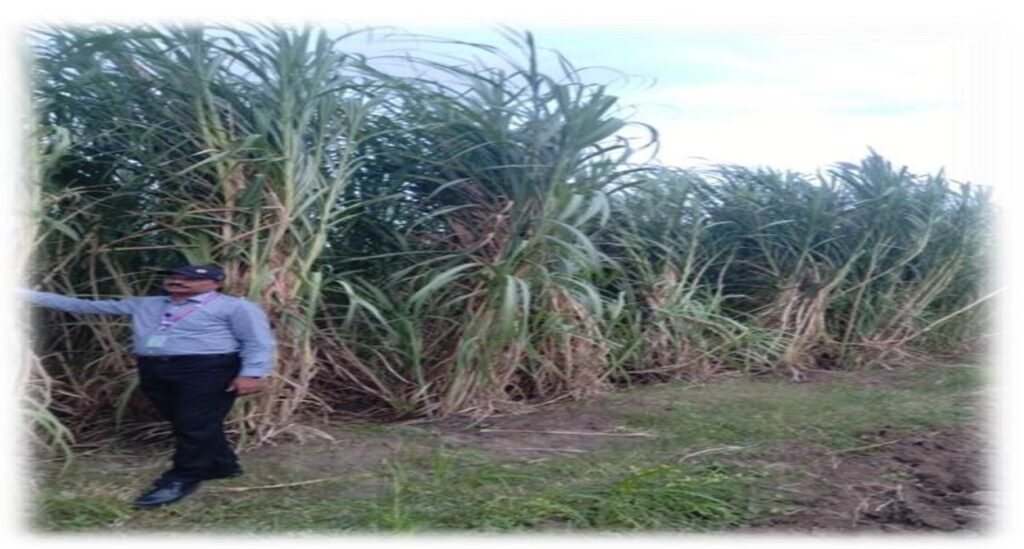
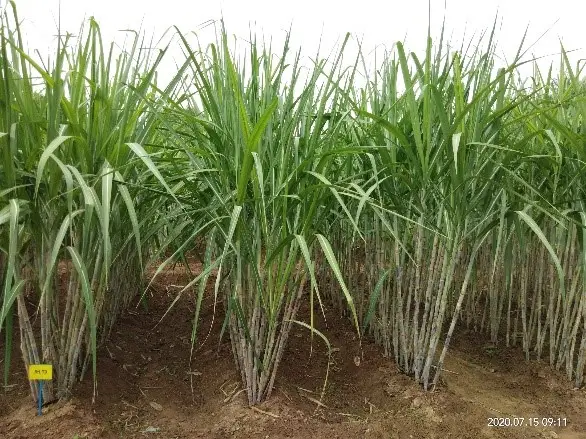
SBIEC14006- Energy Cane
- Type II Energy cane SBIEC 14006 developed at ICAR-SBI, Coimbatore recorded harvestable biomass yield was 284.27 t/ha at 12th months, 2.13 kg Single cane weight (SCW) with trash and tops, 1.38 Kg single cane weight, 395 cm mean cane height and 2.38 cm cane diameter.
- Juice quality parameters such as Brix % and Pol % were10.51% and 7.24% respectively.
- Licensing of Energy Cane SBIEC 14006 was granted to Hriday Hydrogen Power Private Limited, Pune, Maharashtra during November 2024.
Field view of Energy cane SBIEC 14006



Germplasm Registration
New germplasm registered with NBPGR, New Delhi
Three genetic stocks were registered with ICAR-NBPGR, New Delhi during July 2024
Sl.No | Donor identity | National identity | INGR_No | Year | Pedigree | Unique features |
1 | GU 12-21 | IC651997 | INGR24049 | 2024 | GU 04-28EO-2 x Co 06027 | Broad-spectrum resistance to red rot for tropical and sub-tropical isolates with high winter sprouting potential |
2 | GU 12-19 | IC651998 | INGR24050 | 2024 | GU 04-28EO-2 x Co 06027 | Intergeneric hybrid involving Erianthus procerus with high winter sprouting potential and broad-spectrum resistance to red rot |
3 | Co 12014 | IC651999 | INGR24051 | 2024 | Co 97007 x Co 775 | Multiple disease resistance (red rot, smut and yellow leaf disease) |
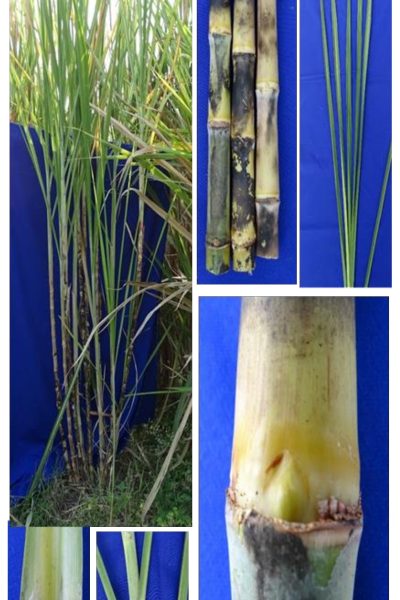

i. GU 12-19
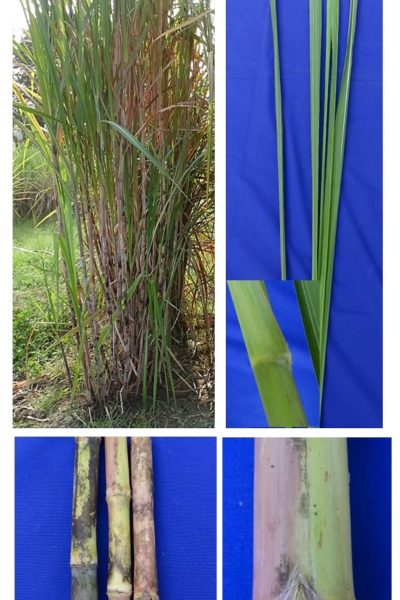

ii. GU 12-21

iii. Co 12014
Maintenance of wild Saccharum germplasm
Maintenance of wild Saccharum germplasm
2277 wild germplasm accessions of Saccharum and allied genera are being maintained at the ICAR SBI Wild Germplasm Repository. This comprise Saccharum spontaneum (1756), Erianthus arundinaceus (233), Erianthus spp. (178), Allied Genera (62) and improved Erianthus clones (48). Forty-seven accessions collected from Arunachal Pradesh are being maintained at IARI Regional Station, Wellington, The Nilgiris.
New initiative in S. spontaneum germplasm management
- This is the state-of-the-art facility for conservation of wild Saccharum germplasm was established during April,2024. Saccharum spontaneum is propagated by root stolons and its maintenance in the field is cumbersome as it spreads to the nearby accessions by its stolons.
- Conventionally spontaneum is maintained by replanting in the field every year. Replanting of huge number of accessions is laborious and time consuming. This concrete ring facility will restrict the root growth within the structure and would help in maintenance of germplasm without any mixing up and could be ratooned for few years once established, thereby reducing the need for every year replanting.
Ex-situ conservation S. spontaneum germplasm at ICAR-SBI, Coimbatore

National Hybridisation Garden (NHG) AT ICAR-SBI, COIMBATORE
National Hybridisation Garden (NHG) AT ICAR-SBI, COIMBATORE
- ICAR- Sugarcane Breeding Institute (SBI) facilitated the 22 participating centres to effect 470 biparental crosses at NHG Centre
- Out of 450 parents in NHG 2024-25, 382 clones flowered with flowering intensity of 84.89 %. The data on different stages of flowering were uploaded in the institute website and updated at weekly intervals to facilitate the centres to plan the crosses.
- 56 kg of fluff (True seed of sugarcane) was supplied to twenty-four fluff receiving centres.
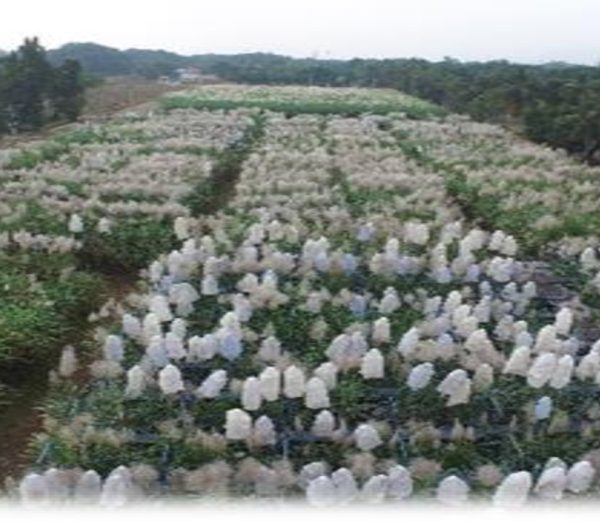

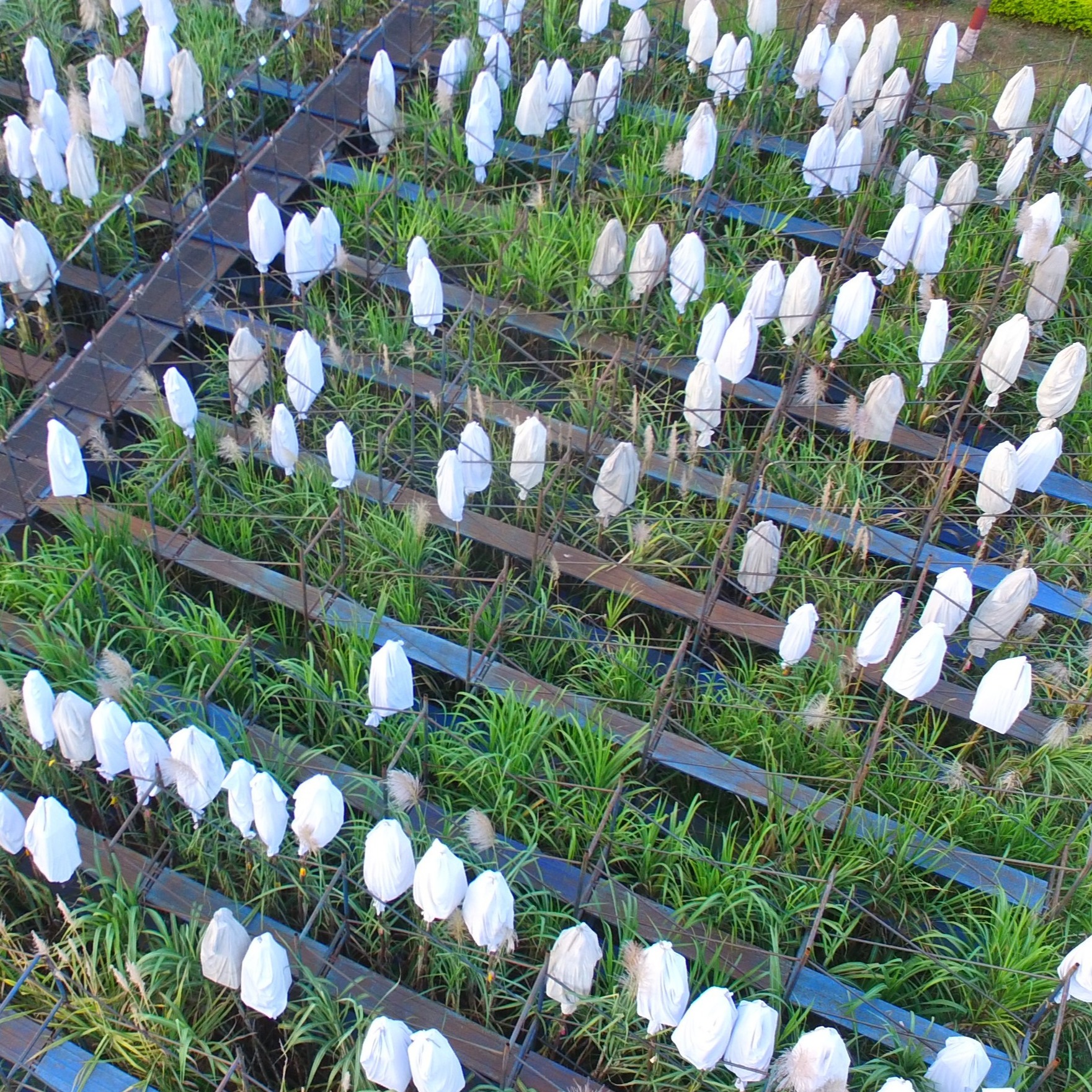
Caging of female parents in NHG during peak flowering season-Drone view
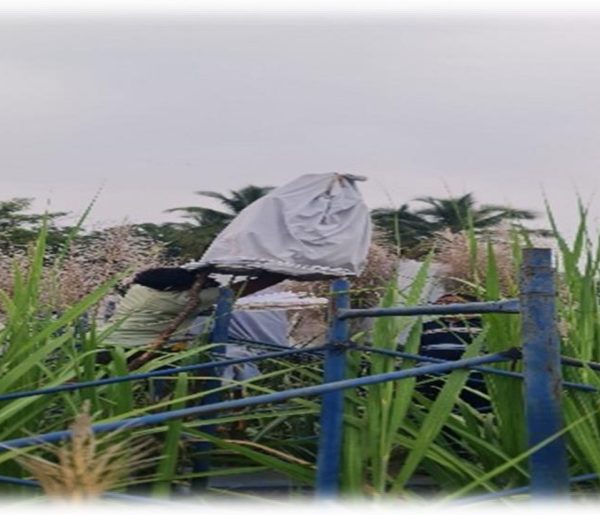

Scientists from participating centres involved in hybridization
New Initiatives under Public Private Partnership Mode
Enhancing Sugar Productivity in Tamil Nadu through Institute- Industry Approach (SISMA-TN funded-SWEET BLOOM 2.0)
Field trials conducted at ten factory locations in Tamil Nadu with seventeen genotypes and local standards identified two promising clones viz., Co 21003 and Co 19009 for Commercial Cane Sugar (CCS) yield, Cane yield and sucrose % across two plant and one ratoon crops during 2023-25 crop seasons
Co 21003
- Co 21003 is a high-yielding, climate-resilient, mid-late sugarcane variety ideal for Tamil Nadu and Puducherry.
- It combines high cane and sugar yields, excellent ratooning ability, and resistance to red rot, smut and YLD.
Co 19009
- High yielding midlate maturing sugarcane variety suitable for Tamil Nadu and Puducherry.
- Resistant (nodal method) and moderately Resistant (plug method) to red rot strains prevalent in Tamil Nadu.

Co 21003

Co 19009
DUS Testing in Sugarcane
Lead Centre- ICAR, SBI, Coimbatore
- The main objective is to establish distinctness, uniformity, and stability (DUS) of candidate sugarcane varieties submitted for registration under the PPV&FR Act, 2001 and to protect the rights of breeders and farmers by verifying the authenticity and novelty of the variety before granting legal protection.
- Eighteen sugarcane candidate varieties have been evaluated so far, comprising ten new varieties (Co 0403, Co 06027, Co 06030, Co 09004, Co 11015, Co 10026, CoA 14321, CoA 14323, MS 17082, and CoM 11082), one extant variety (CoM 0265), and seven farmer varieties (Kudrat ka Karishma, Kaptan Basti, Meitei Chu Angougba, Desi 1, Desi 2, Jeet Katari, and Sugam Katari).
- Eight varieties were registered with PPV&FRA, New Delhi and obtained protection. Currently three varieties are under DUS testing. 250 reference varieties (RVs) of tropical sugarcane are being maintained under field conditions.
Field view of DUS testing trial at ICAR-SBI, Coimbatore

National Active Germplasm (Sugarcane), Icar–Sbi, Coimbatore
NATIONAL ACTIVE GERMPLASM (Sugarcane), ICAR–SBI, Coimbatore
- Sugarcane clones received from different centres were submitted to quarantine, and periodical monitoring are being done.
- 350 notified and registered genetic stocks are being maintained at ICAR-SBI, Coimbatore. 23 clones were assigned index numbers during 2025.
Centralized Research Facilities in Crop Improvement Division
Molecular & Bioinformatics Facilities
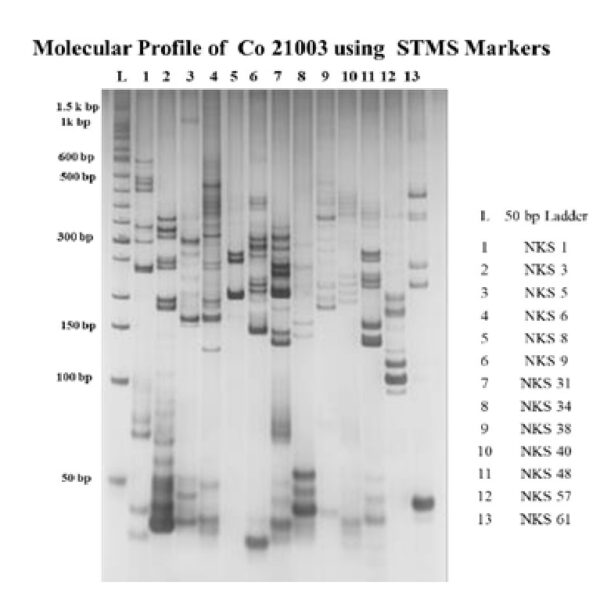
1. Botanical characterization and DNA Fingerprinting
Botanical description for 15 ‘Co’ canes of 2024 series (Co 24001-Co 24015) developed at Coimbatore and its molecular fingerprints were developed.
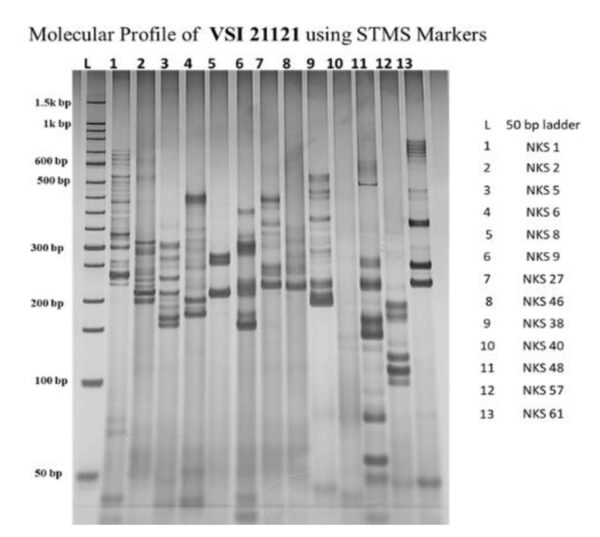
On a payment basis, the molecular fingerprints of VSI 21121, VSI 18008, TC 2513, Co 86032, CoC 671, Co 2000-08 and CoH 20261 were developed during 2025.

2. Bioinformatics facility established for sugarcane genomics and genome editing research
Bioinformatics facility with a high-end server and workstation facility established to support the sugarcane genomics and genome editing research.

Genetic and Cytogenetics
1. Healthy sugarcane seed nursery program: A major flagship program of ICAR Sugarcane Breeding Institute to produce disease free, quality planting material through micropropagation.
Virus free tissue culture seedlings were supplied to private and co-operative sugar factories of Tamil Nadu, sugar factories from other states, breeder seed production and progressive farmers. Tissue culture plants produced at the ICAR-SBI have been well accepted by sugar factories and farmers all over the country because of its uniform productivity, free from viral diseases, vigorous growth and high yield.

2. Genetic stocks registered.: Two genetic stocks (INGR 20070 and INGR 20110 derived with spontaneum registered for Drought tolerance and waterlogging Tolerance.
3. AS 04- 1687 was identified as a multi stress tolerant hybrid for drought, waterlogging, salinity and red rot.
4. A new initiative has been made to describe, identify commercial varieties with digital data base through DELTA (taxonomic) software for the first time in India for agricultural crops.
5. Flowering in Saccharum officiinarum reinvogorated through meristem culture and the mericlones utilised in hybridisation.
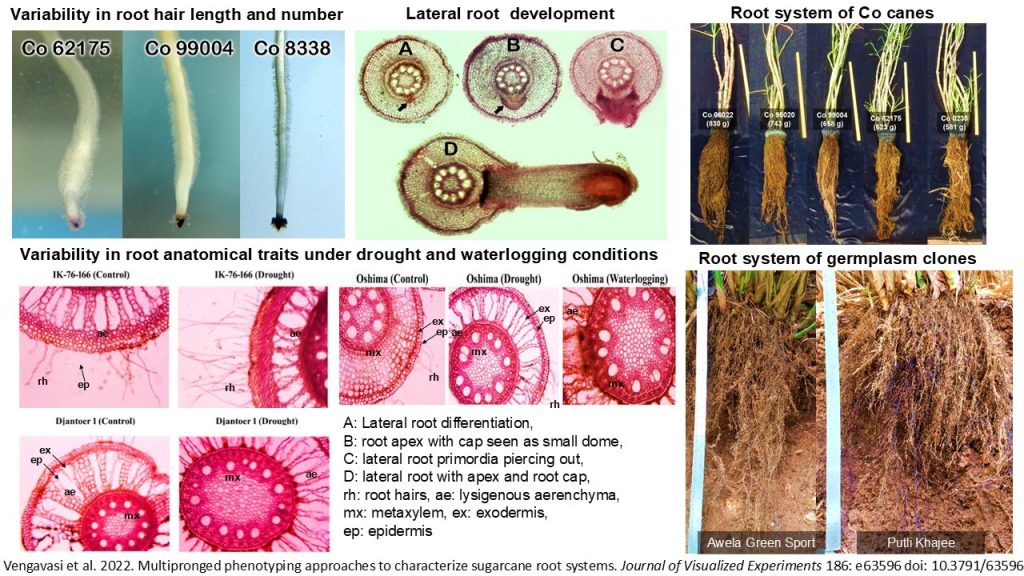
6. Root anatomical traits viz., root hairs frequency, stelar and cortical region ratio and length of aerenchyma were identified as factors influencing drought tolerance.
7. Molecular cytogenetics to study the chromosome introgression in intergeneric hybrids of sugarcane using GISH (Genomic in situ Hybridization) technique
- Amphiploids of E. arundinaceus x S. spontaneum: The GISH analysis of these plants with doubled chromosome number 2n = 124 was found to have 60 arundinaceus chromosomes and 64 S. spontaneum chromosomes.
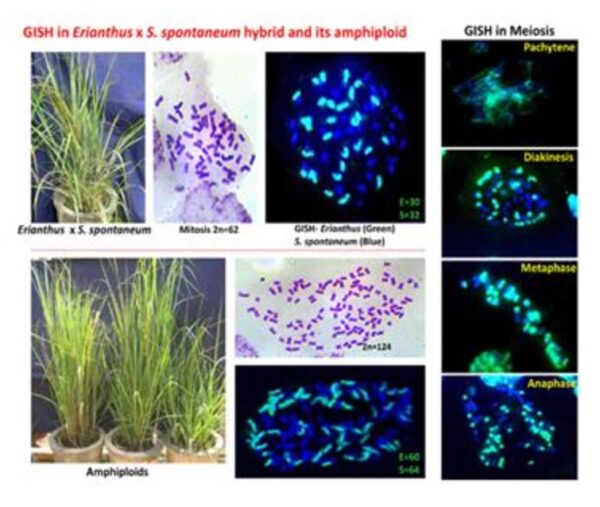

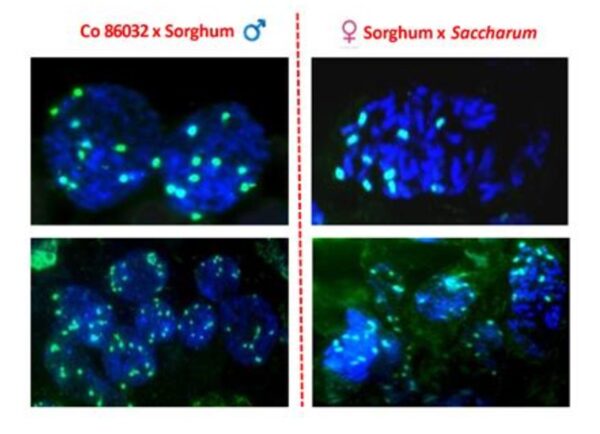
- GISH analysis of Saccharum x Sorghum Co 86032 x SSV 84) and Sorghum x Saccharum (ICSA 56 x IJ 76-316) hybrids identified somatic chromosome number as 2n=66 with ten chromosomes of Sorghum.
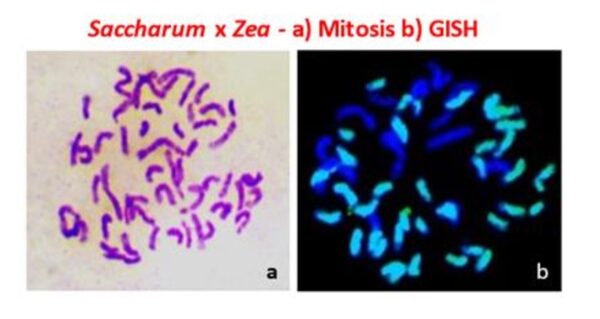
- Tissue culture plants were developed from a rare non flowering hybrid of Saccharum officinarum (Vellai, 2n=80) x Zea mays (Golden Beauty 2n= 20+2B). GISH with Saccharum probe identifies 40 chromosomes of S. officinarum and 10+2B chromosomes of Zea mays in the hybrid.
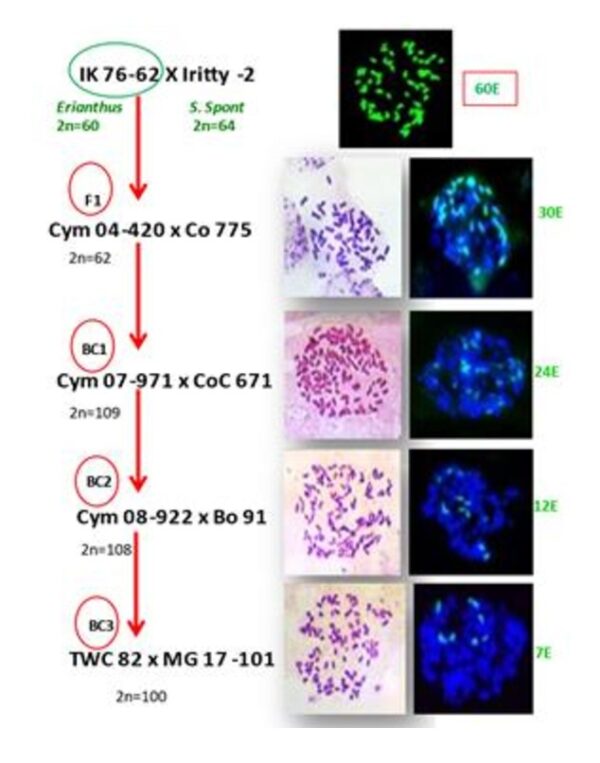
Erianthus arundinaceus x Saccharum hybrids:
Five generations of hybrids involving E. arundinaceus and Saccharum showed the progressive elimination of Erianthus chromosomes in these hybrids. The mode of transmission of gametes, except in the second generation, followed n+n pattern whereas in second generation (CYM 07-971) it was showing 2n+n with elimination of few chromosomes.

Erianthus procerus x Saccharum hybrids:
For the first time the chromosome composition of fertile E. procerus x S. officinarum F1, BC1 and BC2 hybrids via genomic in situ hybridization (GISH) has been studied. The results indicated that the F1 was from 2n+n chromosome transmission, while BC1 and BC2 were from n+n transmission. 2n+n chromosome segregation was also found in four BC2 clones.
8. Developed a simple and efficient cryopreservation method for the long-term storage of Saccharum species
Simple and efficient cryopreservation techniques were optimized for the long-term storage of Saccharum species using three distinct explants of Saccharum species, which include the apical meristem, meristem-derived axillary buds, and dormant nodal buds.

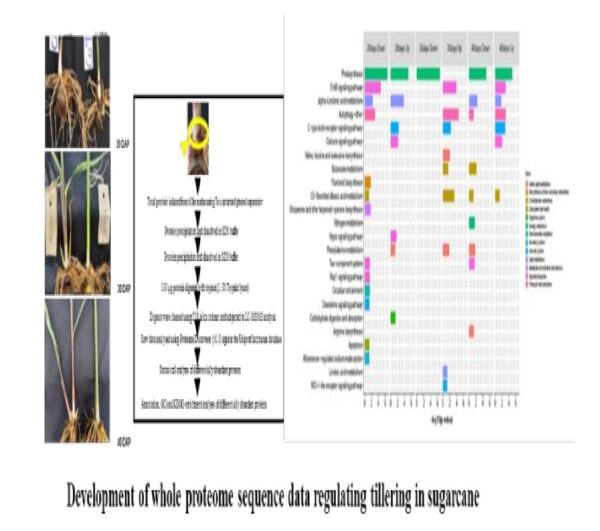
9. Developed first comparative whole proteome data regulating tillering in sugarcane:
Whole proteome profiling of tiller nodes identified important pathways and candidate proteins regulating tillering in sugarcane.
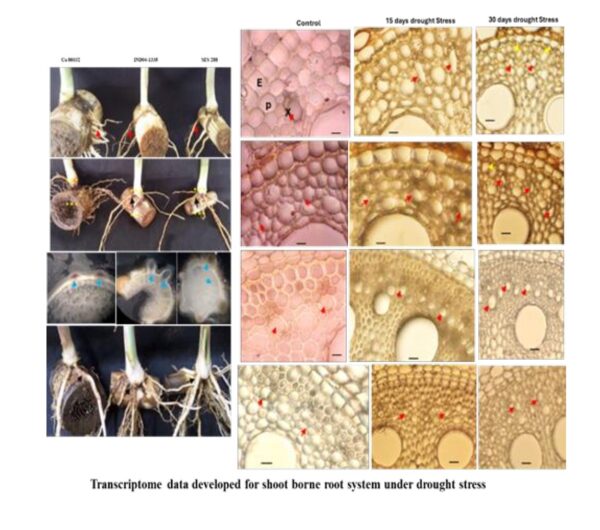
10. Comparative transcriptome profiling to unravel the key molecular signalling pathways and drought adaptive plasticity in shoot borne root system of sugarcane:
A comprehensive whole transcriptome profiling between sugarcane commercial hybrid Co 86032 and wild germplasm Erianthus, identified important stress signalling pathways significantly contributing to enhance water uptake efficiency.
Biotechnology and Bioinformatics
Identification of functionally relevant SSRs and SNP markers and candidate genes for drought tolerance
- A total of 56,646 SSRs and 968 SNPs were mined from the drought transcriptomes of drought-tolerant (Co 06022) and drought-susceptible (Co 8021) sugarcane varieties.
- Seven key drought-responsive genes Dehydrin, TPS, TPP, ABRE, Glyoxyltransferase, Cytochrome P450, and NAC4 were cloned and sequenced for functional validation.
- Morphological, physiological and differential expression analysis of drought-responsive genes in interspecific hybrids and Co cultivars identified AS-04-1687 and AS-04-635 as the most drought-tolerant clones, while AS-04-245 was least tolerant.
- Key stress-related genes such as Dehydrin, DREB, NAC086, GST, ABRE1, and HSP70 showed elevated expression under drought stress. The Dehydrin gene (460 bp) was successfully cloned and sequenced from AS-04-1687, showing high similarity with Saccharum hybrid DHN1 with conserved motifs (K-, Y-, and S-segments).
Genomic selection in sugarcane for red rot resistance and sucrose through SNP markers
- A total of 650 clones from the population of BO 91xCo 775, CoM 0265 x Co 775 , Co 86002 X B0 91, Co 1148 x Co 775 were genotyped with SNP markers in cane chip 44 K array for yield, sucrose content, and red rot resistance.
- Significantly associated Single Nucleotide Markers (4) were identified for red rot resistance sugarcane
- Bayes B genomic selection models with prediction accuracy of 0.58 can be used for selection of red rot resistance.
- Genomic prediction models having prediction accuracy of 0.72 were developed for sucrose content which can predict the sucrose in the seedling population.
- A set of markers with largest effect on red rot resistance was identified in sugarcane. Genes nearby the markers linked to the QTL when investigated for likely biological function revealed many biotic stress responsive genes within this QTL, with the most significant SNP co-locating with a cluster of four chitinase A genes, NBS LRR and DMR region.
Screening Methods & Phenotyping for Oxidative Stress Tolerance in sugarcane, Erianthus sp and S. spontaneum
- A novel screening methodology for oxidative stress tolerance in sugarcane and wild species has been developed. Phenotypic screening for multiple stress tolerance traits such as cell membrane injury (%), leaf temperature, lipid peroxidation (MDA content), SPAD value, and chlorophyll fluorescence (Fm/Fv), along with biochemical screening parameters such as superoxide dismutase (SOD), peroxidase, ascorbate peroxidase, proline content, and soluble protein content, showed that H₂O₂ concentrations of 500 and 1000 ppm for more than 48 hours are critical for inducing oxidative stress in Erianthus arundinaceus and spontaneum.
- For sugarcane, oxidative stress treatment involves the application of 500 ppm of 30% hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂) for 24 hours. For species like spontaneum and Erianthus sp., a more extended treatment period of 48 hours with H₂O₂ concentrations greater than 500 ppm is required. Key traits for this screening methodology include cell membrane injury percentage, leaf temperature, SPAD value, and chlorophyll fluorescence (Fm/Fv).
Biomass modification of sugarcane and salinity tolerance studies
- Novel laccase-producing thermo-tolerant organisms were identified and its culture conditions optimized for effective delignification. Forty-three isolates were screened for ligninolytic activity, and six isolates with higher laccase specific activity (2.26 to 5.49 U mg−1protein) were identified. Maximum enzyme production of 450 U/μL was obtained after 120 hours of incubation, at 46°C and pH 6.0.
- Optimized the laccase enzyme production from Flammulina velutipes using response surface methodology box-behnken design
- Cloned, functionally characterized and studied the expression pattern of phenylalanine ammonia lyase (PAL) involved in lignification of secondary cell wall. PAL gene of 3.2-kb from Erianthus arundinaceus (EaPAL) with an ORF of 2116 bp encoding for 705 amino acid residues flanked by 172 bp of 5’ untranslated region and 300 bp of 3’ untranslated region was obtained.
- Suppression subtractive hybridization (SSH) and sequencing identified salinity induced upregulated transcripts in spontaneum clones from different geographical regions of India which were subsequently validated by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction.
- Functional annotation and pathway analysis revealed that upregulated transcripts viz., UDP glucose dehydrogenase, cellulose synthase, ribulose, cellulose synthase COBRA, leucine-rich protein, NAC domain protein, pectin esterase, ABA-responsive element binding factor 1, and heat stress protein involved in protein modifications, stress, and hormone signalling along with cell wall development and lignification.
CRISPR-Cas based editing of flowering genes
Characterized the full-length gene of FLOWERING LOCUS T Multiplex single-guide RNA (sgRNA) (3) for simultaneous targeting of multiple locus were developed for gene editing using overlap PCR. These constructs were then introduced into sugarcane through transformation (both the methods of Agrobacterium mediated and Particle bombardment) targeting the Flowering Locus T gene. Transformed plants were regenerated and plantlets were developed.

Transformed regenerants of sugarcane with Flowering locus T gene
CRISPR Cas gene editing in sugarcane for haploid induction
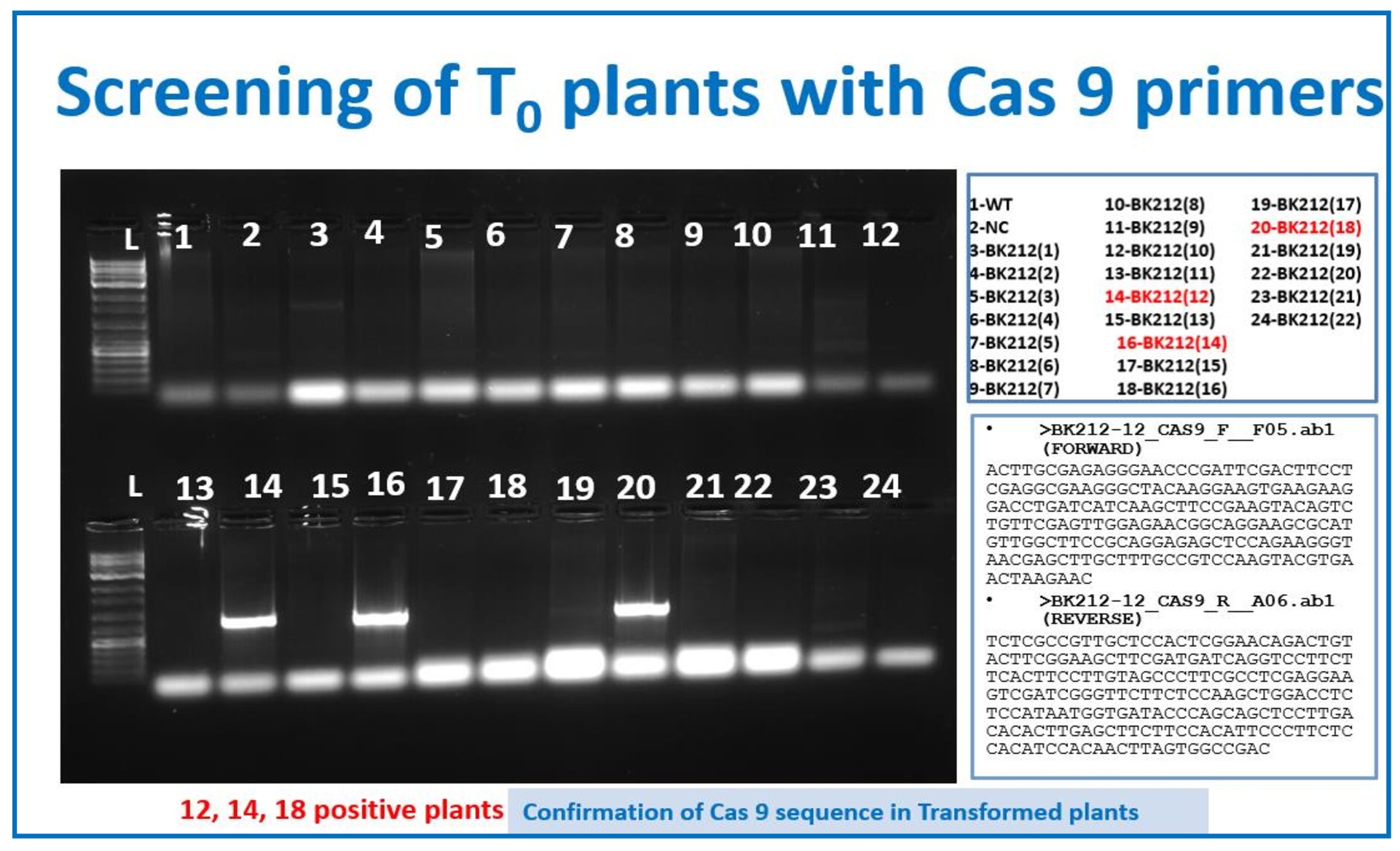
PCR based screening of T0 plants with Cas9 specific primers
Genome wide identification, characterization and comparative genome analyses of SWEET genes regulating sucrose accumulation in sugarcane
- Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of the SWEET gene family from long-read transcriptomes of sugarcane hybrid Co 11015, officinarum, and S. spontaneum was carried out.
- A comparative phylogenetic analysis of SWEETs was performed using the protein sequences from the sugarcane hybrid species Co 11015 and R570, the officinarum, S. spontaneum (Cbe) and S. spontaneum (AP85-441), Sorghum bicolor, and Zea mays.
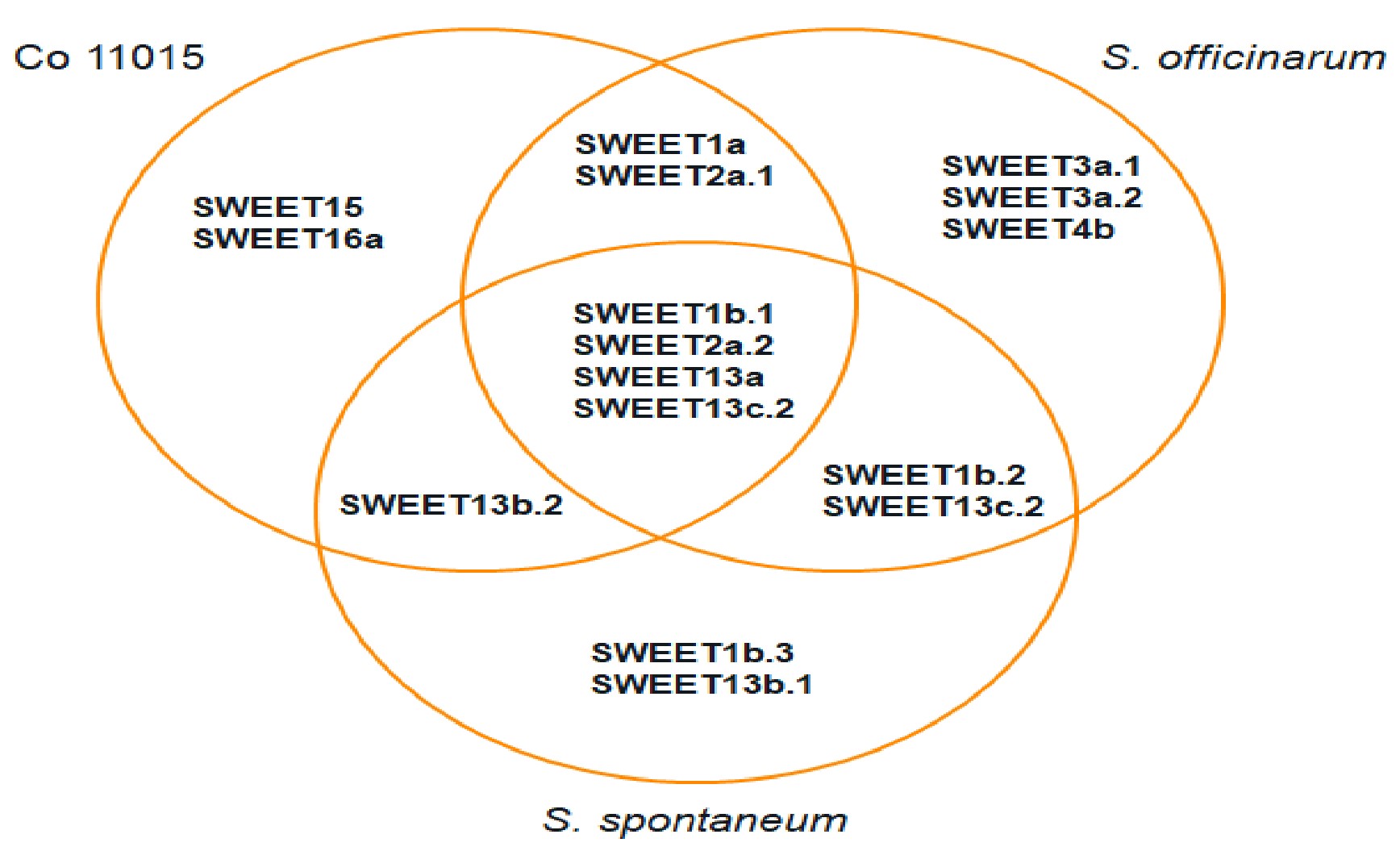
Common and unique SWEET transcript distribution in sugarcane hybrid and progenitor species
Characterization of PP2C genes in sugarcane and related species
- Plant PP2C phosphatases are important proteins in plants and are reported to play a significant role in biotic and abiotic stress responses.
- 500 genes were identified in R570 which were distributed in all 10 chromosomes and its sub genome. All these is named as SoffiXPP2C followed by number based on their order of position on the chromosome.
- Based on the phylogenetic analysis keeping PP2C genes from wild sugarcane, maize, and wheat as a reference, these PP2C genes in modern sugarcane cultivar were classified in to 13 subfamilies.
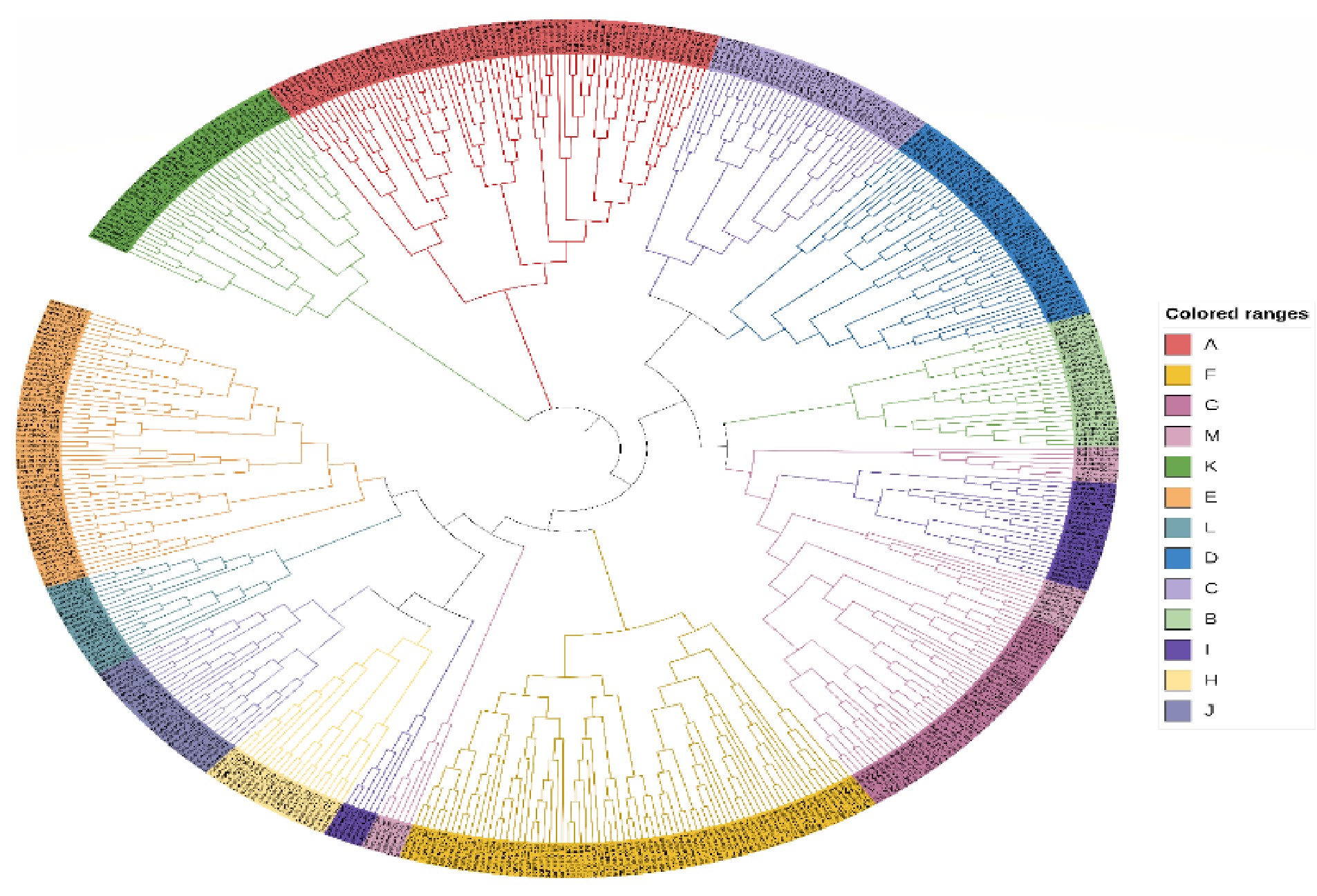
Phylogenetic relationship among the 500 SoffiXPP2C genes
Comparative genomics and bioinformatics tools for abiotic stress tolerance in sugarcane
- Comparative genomic and synteny analyses were carried out among modern hybrid sugarcane cultivar R570 and wild relatives including Saccharum spontaneum (AP85-441), officinarum (LA Purple), and Erianthus fulvus to investigate the genetic basis of salinity and drought tolerance.
- Among the 67 drought-tolerance genes analyzed, 56 orthologs were detected in the hybrid cultivar R570, 56 in officinarum (LA Purple), 49 in S. spontaneum, and 54 in Erianthus.
- Synteny analysis in sugarcane cultivar R570 revealed 1036 genes involved in syntenic relationships forming 1041 pairwise associations and 49 synteny networks for drought-tolerant orthologs.
- In officinarum (LA Purple), 859 genes participated in synteny, yielding 820 pairwise associations and 50 synteny networks corresponding to drought-tolerance orthologs.
Phylogenetic tree for drought stress ortholog in R570 and S. spontaneum

Gene ontology analysis for drought tolerance orthologs in Sugarcane cultivar R 570
Division of Crop Production
Agronomy
Resource Use efficient Sugarcane intercropping system
- Application of 100% N to sugarcane in combination with sugarcane + amaranthus intercropping system is more advantageous in terms of land use efficiency, nitrogen use efficiency, crop yield and economic advantage.
- Sugarcane + amaranthus was found to be a profitable system as the net return (Rs.169,763 ha−1) and B: C ratio (1.78) was higher than all the other system.
- The best combination in terms of B: C ratio is sugarcane + amaranthus as the cost of cultivation is lower and the net return is higher.
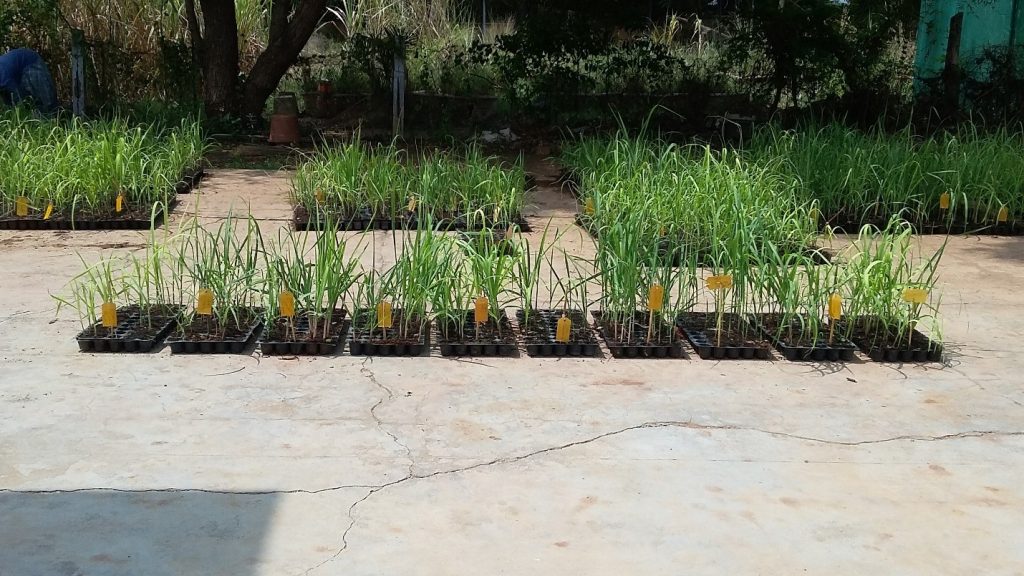
Standardized Planting Agro-techniques for Sugarcane Tissue Culture Plantlets and Bud Chip Settlings (Co-PI)
- Micro-propagated tissue culture plantlets (TCP) recorded higher cane yield than bud chip settling. Planting of tissue culture plantlets with crop geometry of 120 cm x 60 cm and 5.0 cm planting depth was found beneficial in improving cane yield over rest of planting agro-techniques.
- Planting tissue culture plantlets with crop geometry of 120 cm x 60 cm and 5.0 cm planting depth recorded significantly higher mean cane yield (99.3 tha-1) than planting TCP with crop geometry of 120 cm x 45 cm and 2.5 cm planting depth (82.2 t ha-1), whereas planting bud chip settling with crop geometry of 120 cm x 60 cm and 2.5 cm planting depth recorded marginally higher (90.7 t ha-1) mean cane yield than planting BCS with crop geometry of 120 cm x 45 cm and 5.0 cm planting depth (83.9 t ha-1).
Potential growth promoting Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria
- Single bud sett treatments with Beijerinckia spp. recorded a higher germination of 80% when compared to all other bioinoculants with single bud setts. Similar results were obtained with chip buds also, where Beijerinckia recorded, 46% and 58% germination at 20th and 30th days, respectively.
- Sett treatment with bio-inoculants through Sett Treatment Device significantly influenced the settling vigor in single bud and bud chips. Beijernickia recorded the highest settling vigor index in single bud (857.7) and bud chip (437.1) on fresh weight basis.
- Among the bio-inoculants, higher microbial count was observed in Beijernickia spp. Treated setts followed by diazotrophicus (GD) and Methylonbacterium spp. (PPFM).
- Sett treatment with bioinoculants prior to planting in protrays with Beijernickia @ 0.5 ppm has advantage in improving the germination and vigor of sugarcane transplants.

- Developed technology for the production of novel products from sugarcane viz., freeze dried sugarcane juice, cane jam, cane dietary fibre food products, liquid jaggery processing without any chemical additives, novel frozen sugarcane juice products like frozen sugarcane juice, kulfi and softy ice cream and wine
- Associated with the development of a process for producing biopesticide formulation of entomopathogenic nematodes with extended shelf life
- Associated with the development of a standardized novel process for formulating a low-cost scarabid-specific Bacillus thuringiensis biopesticide for management of white grub Holotrichia serrata
Soil Science
- Sugarcane settling transplanting technology
- Sugarcane Settling Transplanting Technology (STT) is a technological combo aimed as a whole to reduce cultivation cost and improve productivity.
- Transplanting settlings (25-30 days old) derived from single bud setts of high yielding better quality variety (Co 11015) in wider row spacing (1.2 x 0.6/0.6 m), intercropping (black gram, green gram, coriander, etc.), drip irrigation scheduling based on crop demand and pan evaporation and fertigation based on soil test crop response, multiple ratooning (up to 5 ratoons), Trash mulching at detrashing, and trash incorporation after harvest of plant and each ratoon crop, and mechanization of field operations from field preparation to harvesting are the cultural practices under STT.
- STT as a package resulted in 80% saving in seed cane requirement and 30% saving in planting cost over sett planting, saving of 52% water, 90% labour cost for irrigation and 50% power consumption over sett planting with furrow irrigation.
- Intercropping resulted in 10-20% improvement in cane yield over sole sugarcane and provided interim and additional income. STT generated benefit cost ratio of 1.93 at the end of five years
- The cane yield with black gram intercropping in plant crop was 147 t/ha and the average cane yield of five ratoons was 93 t/ha under STT.
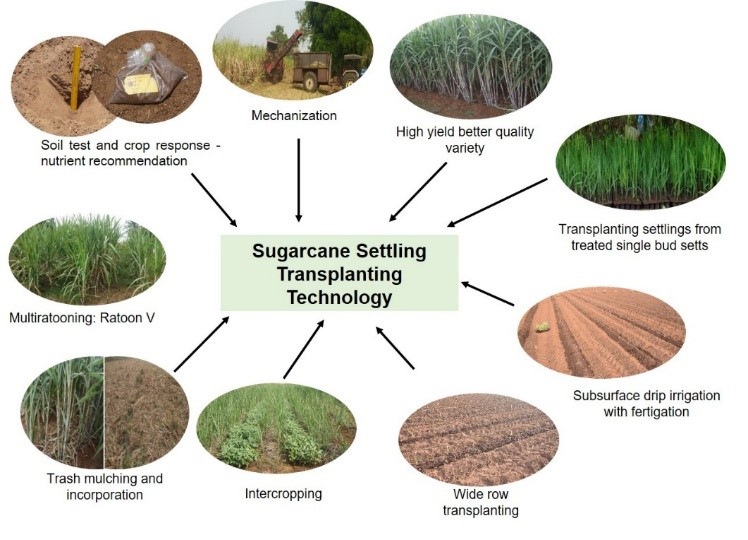
Developers: A. Vennila, S. Anusha, C. Palaniswami, Bakshi Ram, P. Malathi and V. Kasthuri Thilagam
2. Integrated nutrient management package for sugarcane in calcareous soil
- INM package for sugarcane in calcareous soil with soil calcareous amendments was developed.
The Package is
- FYM @ 5 t/ha + elemental sulphur @ 1.0 t/ha as basal for plant crop only, Soil Test Crop Response (STCR) based NPK (P basal, N and K in three splits) with symptomatic spray of Urea, FeSO4 and ZnSO4 for plant and ratoon crop.
(or)
- FYM @ 5 t/ha + gypsum @ 2.50 t/ha as basal for plant crop only, soil test based NPK (P basal, N and K in three splits) with symptomatic spray of Urea, FeSO4 and ZnSO4 for plant and ratoon crop.


Crop stand at 150 DAP with the above INM package
Contributors: A. Vennila, C. Palaniswami, V. Kasthuri Thilagam and I. Rajendran
3.Efficient and Economical way of Nutripriming of Sugarcane Single Bud Setts
- Reuse of same nutrient solution for nutripriming of sugarcane single bud setts up to four cycles in vacuum based treatment to produce vigorous settlings which is evident with nutrient infusion, sett germination, settling biometrics and vigour.
- Two days of advancement in mean germination time provides 15.56% additional settling production with same set of nursery resources.
- This technology saves 75% nutrients and water required for priming, and reduces the preparatory time for treatment, disposal of spent solution, and drudgery involved.
- Multi-location trial conducted at selected Sugar Mills showed average sugarcane yield gain of 5.26%.
Contributors: A. Vennila, P. Malathi, V. Kasthuri Thilagam, C. Palaniswami and R. Viswanathan
4.Soil Inference System (SIS) software for soil constraint management for sugarcane cultivation
- Twenty soil profiles were excavated in sugarcane growing areas of Erode, Tiruppur and Dindigul districts of Tamil Nadu and characterized.
- SIS software with recommendation for soil constraint management for sugarcane was developed using profile characteristics, the general soil fertility categorization, categorization of soil as normal, saline, alkaline, saline-alkaline and calcareous and the soil physical constraints.
- Management measures for subsurface hardening, sulphur nutrition and calcareousness were incorporated apart from nutrient recommendations and problem soil management measures in the SIS.
- The developed SIS software provides soil health card with soil constraint management and nutrient recommendations in Tamil as Microsoft Excel .csv file. This system is developed for printing on template card.
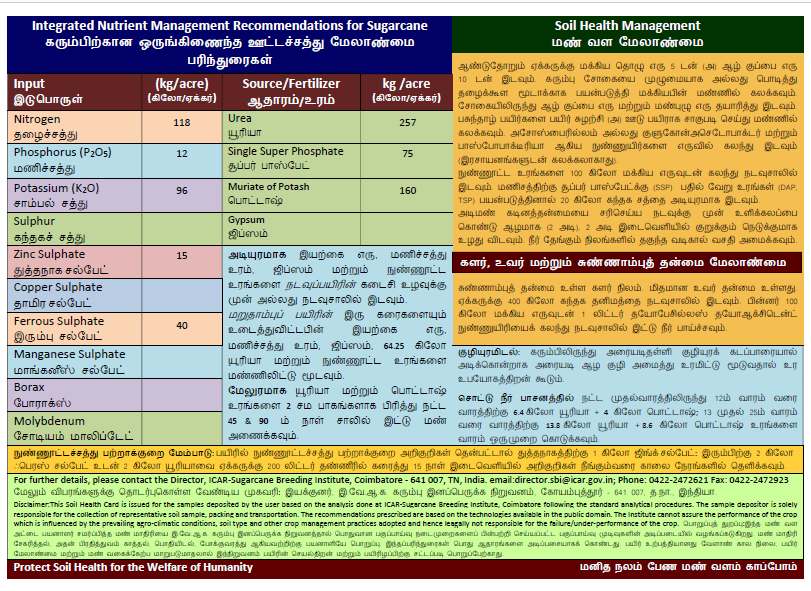

A model soil health card generated using SIS software
Contributors: C. Palaniswami, A. Vennila, A. Bhaskaran, V. Kasthuri Thilagam
5. Soil Smart Sugarcane Management System (SoSmart) software with site specific nutrient and irrigation management for sugarcane.
- SoSmart software was developed with site specific nutrient and irrigation management for sugarcane. This software provides the user with site specific management options for efficient use of inputs based on soil types, climate, variety, planting material, irrigation methods, fertilizer application methods, intercultural operations under sole/intercropped situations, etc.
- The time and quantity of fertilizers and irrigation water to be applied also incorporated in this software on scientific basis.
- The output serves as a ready reckoner for the users with actual date of executing different management measures. Sugarcane farmers, cane official and extension personnel can make use of this software
Contributors: C. Palaniswami, A. Vennila and V. Kasthuri Thilagam
6. DS4M (Decision support system for sustainable sugarcane soil management) software
- DS4M software was developed for providing soil test crop response based recommendation for plant and ratoon crop.
- Fertilizer recommendation for site specific management of soil for sustainable sugarcane production, enhance the resource use efficiency and reduce the environmental pollution.
- Using the DS4M software generated 1079 soil health cards and package of practices for sugarcane and provided to the farmers through the sugar factories in Tamil Nadu.
- From the test verification trial, it is concluded that the nutrient recommendation based on Soil Test Crop Response target yield of 150 t/ha applied P as basal and N & K in two splits (45 and 90 DAP) has the potential to achieve the target yield.
Contributors: A. Bhaskaran, C. Palaniswami and A. Vennila
7. Sulphur recommendation for sugarcane
- Blanket recommendation of S: Application of S @ 50 kg/ha in the form of gypsum or elemental sulphur + Thiobacillus thiooxidans culture is recommended for higher cane yield along with NPK fertilizers.
- S recommendation for calcareous alkaline soils: S application @ 200 kg/ha along with NPK showed cane yield improvement with a corresponding reduction in soil pH indicating S application at higher doses function as an amendment in calcareous alkaline soils with yield improvement of 29% over without S application.
Contributors: A. Bhaskaran, C. Palaniswami, A. Vennila and P. Rakkiyappan
Physiology
Based on the drought screening procedure, each year advanced breeder’s material (AVT/IVT) is being screened for drought tolerance under field conditions by me from 2000- till date (Gomathi and Vasantha 2010a; Gomathi et al 2010b). In the past two decades, 39 IVT and 145 AVT clones were screened for drought tolerance under field conditions, out of which 14 IVT and 43 AVT clones were identified as drought tolerant. Among these, varieties Co 99004 (Damodar), Co 2001-13 (Sulabh), Co 2001-15 (Mangal), Co 0218, Co 0212, Co 06027, Co 06022, Co 06030, Co 09009, Co 10026, Co 12009, Co 13013 and Co 14012 were released for the peninsular zone by the central variety release committee (CVRC) (Gomathi et al. 2016; Gomathi et al., 2020). Co 0212, Co 06030, Co 6022 and Co 09009 varieties were released for Tamil Nadu state.
Identified drought-tolerant genetic stocks (57 cones) could be used as pre-breeding material for developing/ breeding varieties for drought tolerance. A potential source of genetic stocks for drought tolerance: 57 clones viz.,CoJn 86-600, Co 96009, VSI 9/20, Co 97008, Co 99004, Co 99012, Co 2000-01, Co 2000-03, Co 2000-10, CoTl -1358, 93R5, Co 96023, Co 2001-13, Co 2001-09, Co 2001-15, Co 0202, Co 0211, Co 0214, Co 0218, Co 0219, CoSnk 03632, Co 0416, MS 0301, CoN 05071, CoSnk 05104, CoSnk 05101, Co 05001, CoVSI 05122, Co 06022, Co 06010, Co 06013, Co 06015, Co 06027, Co 07015, Co 07010, Co 07009, Co 08008, Co 08009, Co 08020, Co 09007, Co 10015, Co 11001, Co 11005, Co 12009, Co 13013, Co 13009, Co 13002, Co 13018, Co 14016, Co 14002, Co 15006, Co 15007, Co 16009, Co 16010, Co 17013, Co 17012, and Co 17005 are identified as potential genetic sources for drought tolerance under field conditions.
“Co 14012” – A Climate Resilient Superior Variety for Tropical & Sub-Tropical India
Six sub-tropical clones (Co 0238, Co 15023, Co 15027, Co 98014, BO 91 and CoLk 8102) and six tropical clones (Co 11015, Co 0212, Co 06022, Co 13006, Co 14012 and Co 86032) were planted at two different climatic conditions viz., ICAR-Sugarcane Breeding Institute, Cbe (Tropical) and ICAR-SBI Regional Centre, Karnal (sub-tropical) to identify a superior common variety for both tropical and sub-tropical India by assessing physiological efficiency and yield potential at two locations. A comparative pooled analysis of three years of field data at two different locations indicates that some of the biometric traits (tiller production, LAI, plant height, TDMP & its partitioning efficiency), physiological (total chlorophyll content & NR ase activity) and biochemical traits (total phenolics and soluble protein content) were strongly associated with the differences in yield performance when the varieties are grown at different locations. Interestingly, we noticed that some of the physiological factors are common and some of the factors are location specific i.e., tillering potential is not a factor for sub-tropical varieties grown under tropical conditions, however, vice-versa was noticed for tropical varieties grown under sub-tropical conditions. Yield and yield components in tropical conditions revealed that the varieties Co 86032, Co 14012, and Co 11015 in tropical groups and Co 98014 and Co 15027 in sub-tropical groups performed better in NMC, SCW, and cane length and thickness and thus recorded higher yields compared to other varieties studied. Similarly in sub-tropical conditions, Co 15027, Co 0238, and Co 15023 in sub-tropical and Co 14012 and Co 13006 in sub-tropical groups recorded higher yield components and thus recorded higher yields. The results of G X E analysis suggest that Co 14012 and Co 98014 are identified as common varieties for cultivating both tropical and sub-tropical India, however, the latest variety Co 14012 was found superior in morpho-physiological, yield, and quality to Co 98014.
Water efficient sugarcane clones for sustaining sugarcane production under water-limited conditions
The annual water requirement for sugarcane ranges from 1000 to 2900 mm, depending on the agro-ecological conditions, cultivation practices, and crop cycle. In a changing climate, the delay or failure of monsoon has a direct effect on the water available for irrigation. Given these constraints, sustaining sugarcane production is challenging, hence the present study was conducted at ICAR-Sugarcane Breeding Institute, Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu to identify water efficient sugarcane clones for maximizing cane yield under water-limited conditions. Experiments were conducted for four consecutive crop seasons including independent trials for commercial hybrids, and germplasm clones in split plot design, wherein irrigation scheduling was the main plot, and genotypes were accommodated in subplots. A measured quantum of water was applied according to the treatments, monitored using a water meter. Irrigation treatments were initiated at 60 DAP to ensure uniform crop establishment. The irrigation treatments included I0: full irrigation at recommended interval, with 100% crop evapotranspiration (ET) replacement (control); I1: restricted irrigation at recommended interval, and with 50% crop ET replacement (50% by volume). I2: restricted irrigation by skipping alternate irrigations with 50% crop ET replacement (50% by frequency) (Fig. 1A). The clones viz., Co 85019, Co 10026, Co 12009, Co 13014, Co 14002, Co 14025, Co 15015, and Co 15018 were water efficient (> 5 kg/m3), while among the germplasm clones, Fiji 55, ISH 111, ISH 107, Pathri, and Gungera showed better water productivity and lower water footprint in terms of sugarcane production per unit water. Further, estimation of canopy temperature (Fig. 1 B&C) through thermal imaging was identified as a useful trait to screen large breeding populations under water-limited conditions. The results of this study highlight the superior ability of water efficient sugarcane clones to convert water into biomass even under water-limited conditions. The implications of these results are of paramount importance in sustaining sugarcane productivity in water-limited conditions.
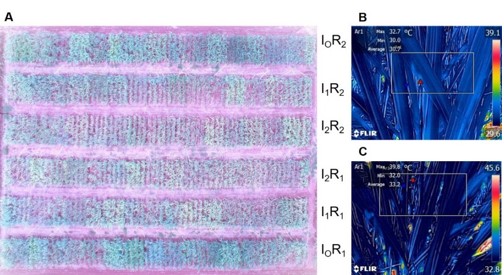
Figure 1 (A) Aerial view of experimental field with treatments I0: control, I1: 50% by volume, I2: 50% by frequency, R1 and R2 denote replications. Thermal image representative of canopy temperature under (B) irrigated and (C) water-limited condition
-
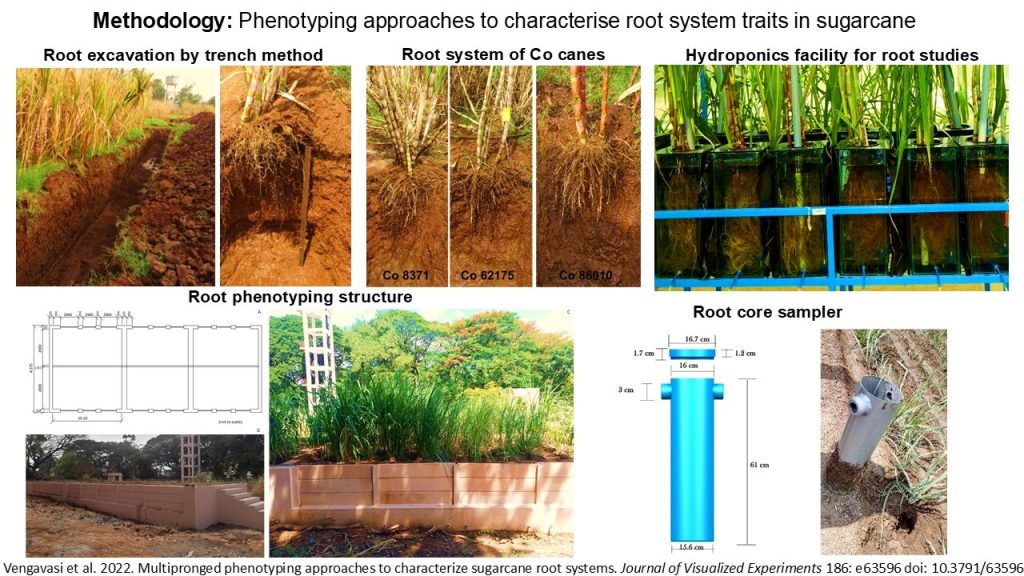
As roots are the most dynamic plant organs, a single methodology to evaluate variation in root phenotypes may not be conclusive, especially in a crop such as sugarcane. The application and integration of suitable permutations of methodologies including field excavation by trench sampling, the use of a root core sampler, raised platforms for root sampling, and raising plants under hydroponic culture.
- Field excavation by trench sampling is imperative to assess the plant roots in their natural growing environment. The use of raised platforms simulating field conditions and a root core sampler are alternative approaches, with a considerable reduction in time, uniform sample size, and less loss of root material. Hydroponic plant culture allows the study of morphology, anatomical features, and rhizosphere biology, including the exudation of organic compounds and microbial interactions.
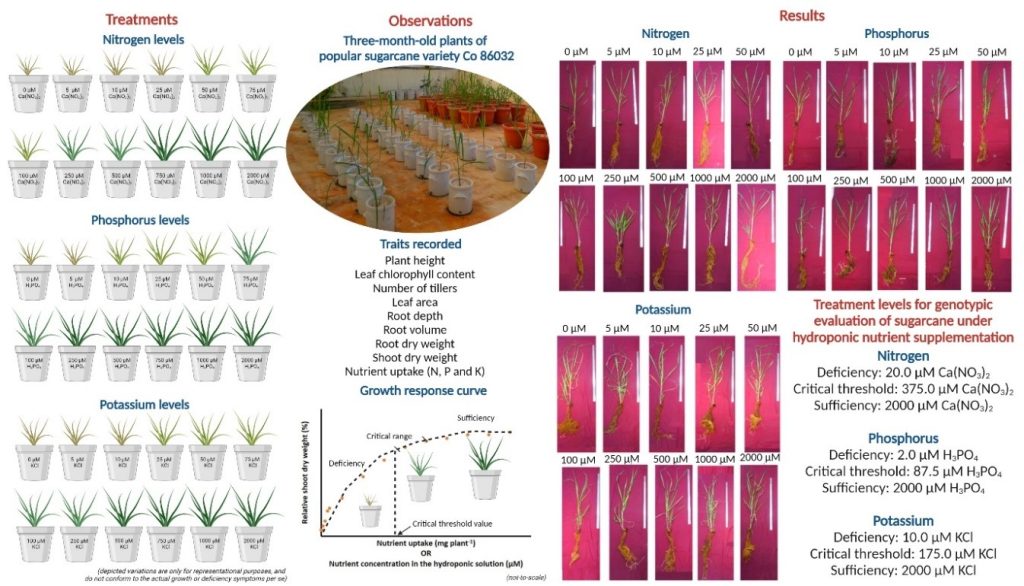 Nutrient efficient sugarcane varieties are required to sustain the yield under optimal fertiliser application with an aim of reducing environmental pollution and conserving natural resources. In this context, it is essential to evaluate sugarcane genotypes at an early crop growth stage for major nutrient (nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K)) use efficiency under controlled conditions. Hydroponic culture facilitates evaluating crops under minimal to nil nutrient levels, thus response to varying levels of N, P and K may be observed earlier as compared to field conditions.
Nutrient efficient sugarcane varieties are required to sustain the yield under optimal fertiliser application with an aim of reducing environmental pollution and conserving natural resources. In this context, it is essential to evaluate sugarcane genotypes at an early crop growth stage for major nutrient (nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K)) use efficiency under controlled conditions. Hydroponic culture facilitates evaluating crops under minimal to nil nutrient levels, thus response to varying levels of N, P and K may be observed earlier as compared to field conditions.- Based on the morpho-physiological responses of Co 86032 to varying levels of major nutrients, hydroponic nutrient supplementation for genotypic evaluation under controlled condition was optimised, including deficiency (20.0 µM N, 2.0 µM P, and 10.0 µM K), critical threshold (375.0 µM N, 87.5 µM P, and 175.0 µM K) and sufficiency (2.0 mM N, P and K) levels.
 Under drought conditions, foliar application of KCL (2.5%) produced a cane yield of 9 t/ha in Co 86032 and 99.0t/ha in Co 0212, which was 18% and 15.2% higher than the untreated drought plot.
Under drought conditions, foliar application of KCL (2.5%) produced a cane yield of 9 t/ha in Co 86032 and 99.0t/ha in Co 0212, which was 18% and 15.2% higher than the untreated drought plot.- Results from the research trial and its validation at farmers’ fields suggested that application of 2.5% KCl positively influenced growth, physiology and cane yield, with higher economic returns compared to the application of bio-stimulants spray and control(No spray)
 Developing heat stress tolerance indices is a prerequisite for sugarcane for screening sources for thermotolerance for future challenging environments. The present technology focuses on studying the whole plant adaptive growth, physiological and metabolic responses to long-term elevated temperature conditions and developing a heat tolerance index for screening thermotolerance for sugarcane. The first systematic global study was conducted on the mechanism of thermo-tolerance in sugarcane at the whole plant level in commercial varieties and wild species clones under artificial conditions.
Developing heat stress tolerance indices is a prerequisite for sugarcane for screening sources for thermotolerance for future challenging environments. The present technology focuses on studying the whole plant adaptive growth, physiological and metabolic responses to long-term elevated temperature conditions and developing a heat tolerance index for screening thermotolerance for sugarcane. The first systematic global study was conducted on the mechanism of thermo-tolerance in sugarcane at the whole plant level in commercial varieties and wild species clones under artificial conditions.- As a result of a five-year multilocational study, developed Heat Tolerance Index (HTI) for screening thermotolerance, including traits such as the stay green nature of index leaf, lipid peroxidation, photochemical activity (Fv/Fm ratio), SPAD value, chlorophyll stability index and total phenolics.
- For the first time in sugarcane, screening methodology and phenotyping for oxidative stress were standardised using hydrogen peroxide. H2O2 concentrations of 500 and 1000 ppm at 48 hours are identified as critical concentrations for inducing oxidative stress in Erianthus arundinaceus and S. spontaneum respectively.
- Physiological traits viz., chlorophyll fluorescence (Fv/Fm), and chlorophyll stability index (CSI) are the key physiological traits for screening oxidative stress tolerance. Assay on soluble protein and reactive oxygen species scavenging enzyme activities like superoxide dismutase (SOD), ascorbate peroxidase (APX) and Lipid peroxidation are the key biochemical indices for identifying oxidative stress tolerance in sugarcane.
- Molecular techniques have revolutionised our understanding of the interactions between genes, proteins, and metabolites, and have aided in the identification of the key regulators of diverse traits. In this process, the next-generation sequencing method RNA-Seq was used to analyse the transcripts of sugarcane and characterise candidate genes related to heat stress for the first time globally.
Identified several novel transcripts which are differentially expressed under heat stress, registered in NCBI for public use. Analysis of relative gene expression studies showed phytepsin, ferredoxin-dependent glutamate synthase, and stress protein DDR-48 threefold increased expression during heat stress. The results of proteiomic study conclude the stress-related proteins including Hypothetical protein (function unknown), Thioredoxin O2 (protects structure and function of cellular proteins) and Cyclin-dependent kinase F (CDKs)-2 (stress signal perception) showed 1.4-, 1.2- and 1.0-fold up- regulation in transcript expression, respectively indicating their greater abundance under heat stress conditions. These findings reveal novel targets for subsequent research on the genomics, genetic manipulation, and molecular mechanisms of elevated stress tolerance in sugarcane
- A comparative analysis of field data at two different locations(tropical and sb-tropical) indicates that some of the biometric traits (tiller production, SGR, LAI, plant height, TDMP & its partitioning efficiency), physiological (total chlorophyll content & NR ase activity) and biochemical traits (total phenolics and soluble protein content) were strongly associated with the differences in yield performance when the varieties are grown at different locations. Some of the physiological factors are common, and some of the factors are location-specific, i.e., tillering potential is not a factor for sub-tropical varieties grown under tropical conditions; however, vice-versa was noticed for tropical varieties grown under sub-tropical conditions.
- Yield and yield components in tropical conditions revealed that the tropical varieties Co 86032, Co 14012, and Co 11015 and sub-tropical varieties Co 98014 and Co 15027 performed better compared to other varieties studied.
- Similarly, in sub-tropical conditions, Co 15027, Co 0238 and Co 15023 in sub-tropical and Co 14012 and Co 13006 in sub-tropical groups recorded higher yield components and thus recorded higher yields. The results of G X E analysis suggest that Co 14012 and Co 98014 are identified as common varieties for cultivating both tropical and sub-tropical India, however, the latest variety Co 14012 was found superior in morpho-physiological, yield and quality to Co 98014.
- Based on our study, the identified Co 14012 is being utilized in the breeding programme for developing climate-resilient sugarcane clones and the same variety is currently evaluated for the multilocational trail in both tropical and Sub-tropical conditions for adaptability and stability for yield and quality.
Weed management in sugarcane under wide row planting

Photo (A)Field view of sugarcane variety Co 86032 at 15 days after planting (DAP), (B) Effect of early post-emergence application of metribuzin at 45 DAP (at the time of partial earthing up) (C) T8 (unweeded control) at 45 DAP, (D) Weed infestation before application of herbicides at 65 DAP, (E) T1 (Topramezone + atrazine) + hand weeding at 160 DAP, (F) T3 (Tembotrione + atrazine) + hand weeding at 160 DAP, (G) T5 (Halosulfuron methyl + metribuzin) + hand weeding at 160 DAP, (H): T7 Three hand weeding at 160 DAP, (I) Unweeded control at 160 DAP
Research findings details
- Severe weed infestations in widely spaced sugarcane plant crops can be effectively managed through an integrated approach involving a sequential application strategy with an early post-emergence application of metribuzin at 1250 g a.i. ha⁻¹ at 10 days after planting (DAP), followed by a post-emergence tank mix application at 65 DAP.
- The tank mix may consist of either topramezone at 29.4 g a.i. ha⁻¹ + atrazine at 625 g a.i. ha⁻¹, or tembotrione at 120 g a.i. ha⁻¹ + atrazine at 625 g a.i. ha⁻¹, or halosulfuron methyl at 67.5 g a.i. ha⁻¹ + metribuzin at 525 g a.i. ha⁻¹. This is followed by one hand weeding at 120 DAP.
- This integrated approach is highly cost-effective, offering a higher benefit-cost ratio, superior weed control efficiency, and broad-spectrum weed management. Importantly, no phytotoxic effects were observed, and significant improvements in cane growth and yield were recorded with 60% reduction in manual labor requirements, contributing to overall farm efficiency.
A simple and sensitive chromatographic method to determine the residues of halosulfuron-methyl in the soil matrix.
Research findings details
- The method developed complies with European Commission’s regulations for Trace Residue Analysis.
- By adopting this method, the persistence and dissipation kinetics of halosulfuron-methyl was studied. The initial deposits of halosulfuron-methyl were 0.288 and 0.501 µgg-1 at the recommended dose (RD) and double the recommended dose (2RD), respectively. A week after application (7 DAA), the residues were 0.177 and 0.346 µgg-1, respectively for RD and 2RD.
- The residues got dissipated to a level of about 95% within 75 days of application with the half-life of 8.85 and 9.12 days.
Commercialised Technology
- Developed technology for the production of novel products from sugarcane viz., freeze dried sugarcane juice, cane jam, cane dietary fibre food products, liquid jaggery processing without any chemical additives, novel frozen sugarcane juice products like frozen sugarcane juice, kulfi and softy ice cream and wine
- Associated with the development of a process for producing biopesticide formulation of entomopathogenic nematodes with extended shelf life
- Associated with the development of standardized novel process for formulating a low-cost scarabid-specific bacillus thuringiensis biopesticide for management of white grub Holotrichia serrata
Division of Crop Protection
Plant Pathology
Achievement of Plant Pathology from 2000-2025
- Multiplex RT-PCR technique was standardized for the detection and diagnosis of individual sugarcane viruses in a mixed reaction of 3 different viruses (SCMV, SCSMV, SCYLV).
- Complete genome (~ 5875 bp) of four SCYLV isolates from infected leaves of Co 86032, CoC 85061, CoV 92102 and B38192 was sequenced and characterized.
- Many sugarcane clones meant for breeding purpose have been tested under CCT for red rot resistance and many PZVT clones were also tested for red rot resistance under field conditions.
- Phenotypical grouping of Sporisorium scitamineum isolates representing different geographical locations based on virulence index was established based on differential interaction studies. Polymorphism among the isolates with SSR and ISSR markers indicated grouping of isolates based on geographical regions.
- Sett treatment devise for mechanized treatment of sugarcane setts was developed for disease management and also production of disease-free healthy nursery
- A methodology has been standardized for synthesis of chitosan nano particles by ion gelation technique. Nano formulations of Benzothiadiazole (BTH) and salicylic acid (SA) was found effective in inducing the host resistance of sugarcane crop against red rot, smut and wilt diseases.
- In the area of molecular virology, virus suppressor proteins in RNA viruses infecting sugarcane P0 gene of SCYLV, P1 and HC-Pro genes of SCSMV were characterized. silencing assays of these suppressor genes proved that both genes have the RNA silencing suppressor activity.
- Endophytic bacteria were identified for red rot and smut management and growth promotion.
- The GC/MS, FT-IR and NMR analyses of pure fraction of Colletotrichum falcatum toxin and its structural elucidation identified the compound as 1,2-Benzenedicarboxylic acid, bis (2-ethylhexyl) ester, thus confirming its role in pathogenesis.
- First time standardized the protein extraction method for protein of sugarcane stalk in the world.
- Suppression subtractive hybridization (SSH) analysis resulted in identification and characterization of genes related to pathogenicity in C. falcatum. Similarly, proteome profiling of C. falcatum representing distinct virulence pathotypes led to identification of proteins related to pathogenicity viz. peptidyl prolyl cis/trans isomerase, fungal specific transcription factor, etc.
- A new SCGS phytoplasma sub group has been identified through in silico RFLP using iphyclassifier
- RT LAMP assay has been developed for SCMV and SCSMV and its sensitivity with the conventional RT PCR and qRT-PCR has been standardized for the mosaic disease diagnosis.
- Novel miRNAs viz RC-709, R6-827, R241288, SC 960, S6-682, and S24-456 involved in sugarcane and C. falcatum interaction were identified. A critical analysis of the role of sugarcane miRNAs during compatible and incompatible interactions by adopting NGS platform revealed the role of sugarcane miRNAs and their target genes during sugarcane C. falcatum interactions and provided new insight into the miRNA mediated defense mechanism in sugarcane.
- Azole fungicides as inhibitor of Cytochorome P450 gene in C. falcatum has been proved under invitro and invivo conditions.
- Nanoparticle enhanced lateral flow immunoassay (LFA) methodologies were standardized for rapid on-site detection of sugarcane streak mosaic virus (SCSMV) associated with mosaic in sugarcane. The sensitivity of this assay was also validated along with other diagnostic methods like qRT-PCR and ELISA.
- A visual calorimetric RT-LAMP: assays were standardized for the diagnosis of SCYLV, SCMV and SCSMV in sugarcane.
- The presence of rust resistant gene Bru1 in sugarcane parental clones maintained at ICAR-SBI, was studied using the marker R12H16 and 9020-F4-PCR-Rsa1,
- CfPDIP1, a novel secreted protein of Colletotrichum falcatum, that elicits defence responses in sugarcane and triggers hypersensitive response in tobacco was identified.
- In the molecular elucidation of biotic elicitor mediated defence responsive genes/proteins, a low molecular weight (LMW) protein fraction of around 10-30 kDa was identified to possess the ability to induce defence in sugarcane.
- Whole genome (48.2 mb) and transcriptome (27 mb) of C. falcatum were generated using next generation sequencing (NGS) technology.
- PCR based diagnostic technique was standardised for the GSD and SCBV and Tissue blot immune assay was standardised for RSD.
- ELISA technique standardised for RSD, SCBV and SCYLV.
- Evaporative binding immunosorbent assay was standardised to detect RSD.
- Dot blot technique for detection of leaf scald disease was standardised.
- Though proteomic analysis of a compatible interaction between sugarcane and S. scitamineum identified 53 sugarcane proteins identified were related to defence, stress, metabolism, protein folding, energy, and cell division; in addition, a putative effector of S. scitamineum, chorismate mutase, was identified.
Entomology
Significant achievements
Biological control
- Entomopathogens
- Prospecting studies for isolation of novel Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) discovered a new indigenous Bt isolate Bt 8 and Bt 84 possessing cry9Da and cry9Eb These Bt’s were found toxic to early shoot borer and internode borer of sugarcane. Transgenic sugarcane is being currently developed at ICAR SBI based on cry9Eb gene for internode borer
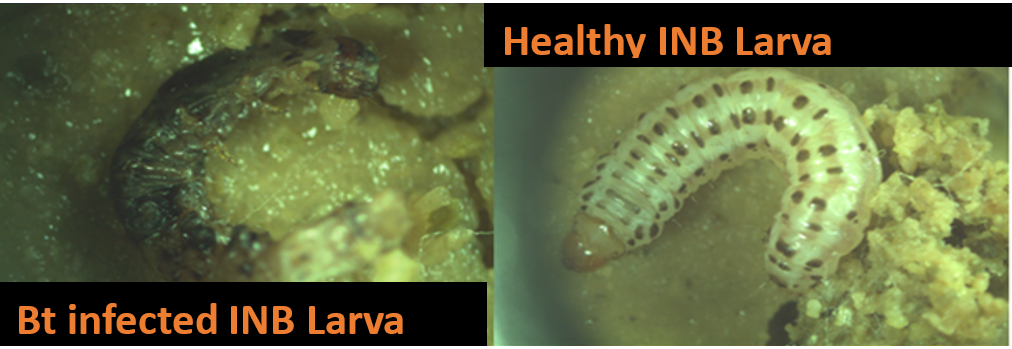
- A novel Bt isolate Bt 62 was isolated against the white grub Holotrichia serrata a major polyphagous pest causing serious economic damage in sugarcane. From this isolate a novel holotype crystal toxin gene cry8Sa1 was isolated and the toxin from this gene was expressed and found toxic to H. serrata. and H. consanguinea. White grub resistant transgenic sugarcane is being currently developed at ICAR SBI based on this gene.
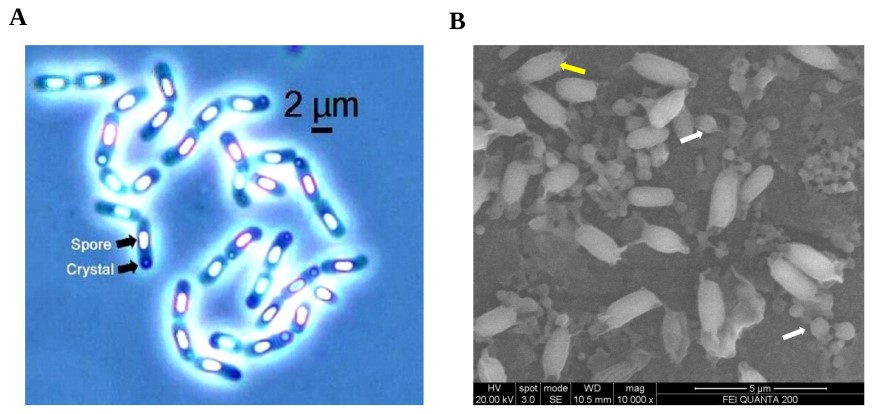
Microscopic analysis of Bt 62 crystal toxin: (A) Phase contrast microscopic images 1000x; (B) scanning electron micrograph of autolysed endospore and spherical crystal toxin; arrows indicate spore (yellow) and crystal (white)
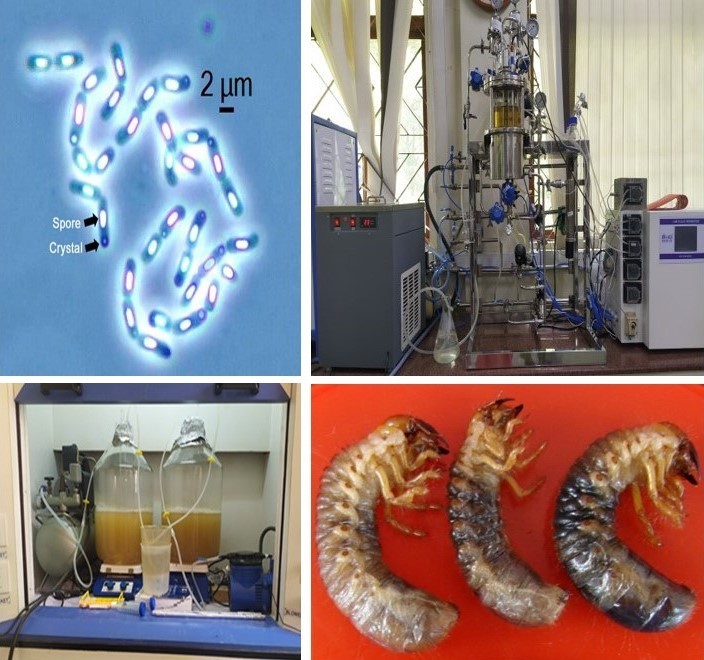
- A Bacillus thuringiensis-based bio-insecticide formulation from Bt isolate Bt-62 which contains the novel coleopteran-specific crystal toxin Cry8Sa1 against white grub Holotrichia serrata was developed. The low-cost technology for mass production of Bt-62 was developed using agro-industrial by-products and sugarcane by-products. Toxicity of the product observed in laboratory studies and efficacy demonstrated in field trials against serrata illustrated that the formulation can be mass-produced and used for the control of Holotrichia serrata.
- A novel diet incorporation method of bioassays for the white grub sp. Holotrichia serrata, consanguinea and other white grub sp has been developed. The method indicated significant toxicity to first and second instar grubs over other method of bioassay as a substitute or supplement to the carrot disc contamination method.

2) Parasitoids
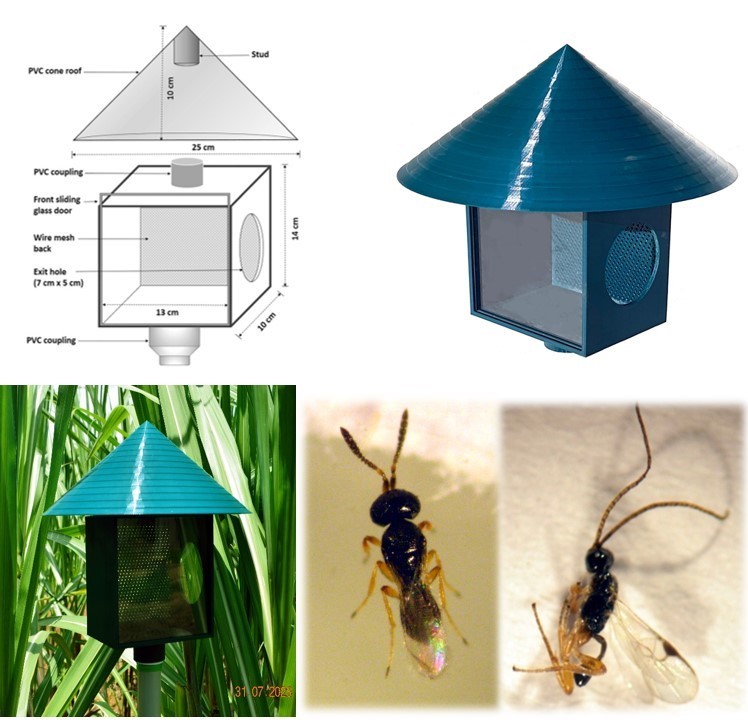
- Mass Production Technology of Cotesia flavipes and Telenomus dignus for Integrated Control of Sugarcane Internode Borer was developed for the integrated control of internode borer egg and larval stages. The usefulness of these parasitoids in internode borer control as single tactic and also in combination through augmentative releases had been demonstrated. Parasitoid releases enhanced parasitism rates and reduced internode borer attack.

- Field-release station for dispensing parasitoids in the field for pest control in crops. The field-release station technology can enhance the control of pest in sugarcane ecosystem by effecting natural control and offers scope for applied biological control via field colonization. The use of this device to dispense the cocoons will prevent injury to the parasitoids released as adults
Parasitoids of Sugarcane Mealybug, Phenacoccus saccharifolii
The mealybug, Phenacoccus saccharifolii has become a major threat to cane cultivation in India and Tamil Nadu, in particular. ICAR-SBI has made in-depth studies on almost all aspects of this pest viz., biology, ecology, yield loss assessment, varietal screening, parasitoid identification and insecticide evaluation. The female individuals complete their life cycle in around 39 days as against only 22 days for male. The yield loss due to this mealybug species has been estimated to be around 7 tonnes/ha at 10% level of its incidence in the ratoon crop. All the varieties under cultivation support the growth and envelopment of this species. However, among the popular varieties, Co 09356 is highly susceptible and Co 86032 is less susceptible. Ratoon crop suffers more when compared to plant crop. Among the several species of parasitoids, Leptomastix sylvae is the dominant one with considerable extent of parasitism. The neonicotinoid insecticide thiamethoxam may be used to manage this species.
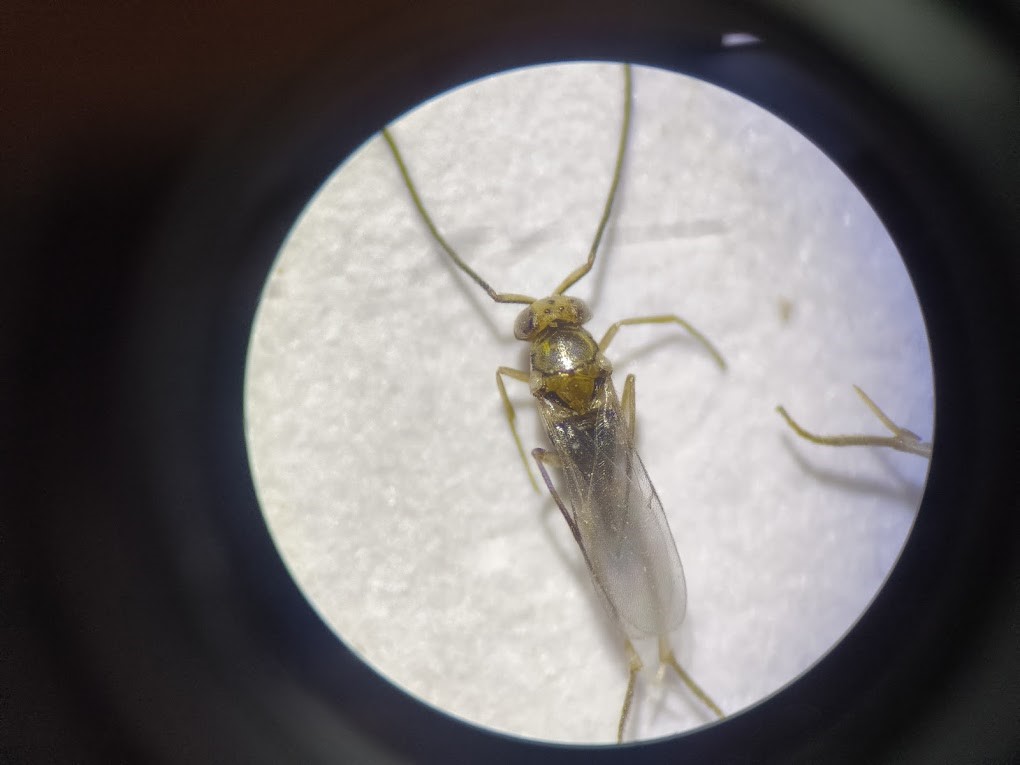

Leptomastix sylvae
Host Plant Resistance
(i) Proteinase Inhibitors as potential biochemical markers for the early detection of borer tolerance and susceptibility in sugarcane genotypes
A sugarcane wild relative Erianthus arundinaceus was identified as a source of resistance against sugarcane tissue borers (early shoot borer (ESB) and internode borer (INB)). Proteinase inhibitors were extracted from borers tolerant E. arundinaceus and their inhibitory activity assessed against commercial trypsin enzyme and midgut protease of sugarcane borers. PIs were maximum in meristem followed by leaf sheath and stalk tissue of E. arundinaceus. Subsequently, extracted meristem and stalk tissue PIs were assayed against midgut protease of shoot borer and internode borer. The results showed that E. arundinaceus meristem PIs significantly inhibit the midgut protease of ESB and INB resulting upto >70% and >60%, respectively. Among the genotypes, PIs were considerably higher in apical meristem and leaf sheath of IJ 76 370 and IJ 76 364 which show strong inhibitory activity against gut proteinase of sugarcane ESB & INB. Correspondingly, shoot borer developmental characteristics were studied in the borer tolerant E. arundinaceus. A significant reduction of larval and pupal survival along with extended larval duration was observed in the genotypes IJ 76 370 and IJ 76 364. In correlation studies, both borers larval and pupal survival were negatively correlated with apical meristem PIs of E. arundinaceus. Similarly, significant positive correlations were found between ESB and INB developmental period with apical meristem PIs of E. arundinaceus. In conclusion, PIs identified from E. arundinaceus could be used as a biochemical marker for the early detection of borers tolerant and susceptible sugarcane varieties. Also, identified two elite genotypes IJ 76 370 and IJ 76 364 which could be used as donors for sugarcane pre-breeding programme for the development of shoot borer resistant varieties. Besides, it could be possible to identify the novel insecticidal proteins (PIs) that may be utilized in genetic manipulation work for producing transgenics imparting resistance against sugarcane borers.
(ii) Screening of popular sugarcane varieties for resistance against borer pests
Seven popular sugarcane varieties grown in India were screened for resistance to early shoot borer (ESB), Chilo infuscatellus (Snellen), and internode borer (INB), Chilo sacchariphagus indicus (Kapur) (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). Of these, five (Co 11015, Co 0212, Co 86032, Co 0238, and Co 09004) are commercial sugarcane hybrids (CSH), and two (Co 06030, Co 06022) are Erianthus-derived commercial hybrids (CSHE). Field screening showed significantly lower ESB and INB incidences in Erianthus-introgressed CSHs compared to Saccharum. INB infestation consistently reduced internode length and girth in all hybrids, while tunneling length did not differ significantly between Saccharum and Erianthus inbreds. Varieties Co 06030 and Co 06022, derived from Erianthus, negatively affected the growth and development of ESB and INB. Similarly, the commercial variety Co 0238 showed reduced borer survival and extended larval development. Increased levels of secondary metabolites viz.,phenols, proteinase inhibitors (PIs), PPO, and silicon in these varieties likely hinder ESB and INB development, indicating antibiosis-based resistance. Correlation studies confirmed that PIs, silicon, and phenols were negatively correlated with borer incidence and development, while total sugars showed a positive correlation. The study identified Co 06030 and Co 06022, derived from Erianthus, as moderately tolerant to sugarcane borers. These varieties could be cultivated in borer-endemic areas as well as included in the sugarcane IPM programme.
(iii) Identification of borer-resistant energy canes as potential sources for biofuel production
A total of 26 newly developed energy canes-Type I (Saccharum spontaneum-derived) and Type II (Erianthus arundinaceus-derived)-were screened against the early shoot borer (Chilo infuscatellus) and internode borer (Chilo sacchariphagus indicus). Field and laboratory studies showed markedly lower borer incidence in Type II canes without affecting internode morphology, while insects reared on them exhibited reduced larval and pupal survival, indicating antibiosis mechanism of resistance. Resistance was associated with higher levels of phenols, silicon, polyphenol oxidase, and proteinase inhibitors, along with reduced nutritive compounds; notably, E. arundinaceus proteinase inhibitors strongly inhibited borer midgut proteases. Significant negative correlations were observed between defensive compounds and borer incidence. Four elite borer-tolerant clones were identified—three Type II (SBIEC 14006, SBIEC 11004, SBIEC 11001) and one Type I (SBIEC 13010) which can serve as potential candidates for biofuel production and also serve as valuable genetic resources for developing borer-resistant energy canes.
(iv) Evaluation of intergeneric sugarcane hybrids (IGHs) for resistance to borer pests
Fifteen intergeneric sugarcane hybrids (IGHs) involving Erianthus arundinaceus were screened against early shoot borer Chilo infuscatellus and internode borer Chilo sacchariphagus indicus under field conditions. Among them, five genotypes viz., CYM 06-212, CYM 08-922, CYM 04-388, CYM 07-971 and CYM 08-314 were free from ESB attack. Similarly, three genotypes CYM 06-212, CYM 69 24 and CYM 08-314 were totally free from INB attack. In the lab screening, despite the severe ESB infestation, the genotype CYM 08-922 showed >90% plants survivability. Similarly, A total of 89 BC2 progenies of intergeneric sugarcane hybrids (IGHs) involving Erianthus procerus were screened against INB under drought and controlled field conditions. In the entries, 11, 24 and 54 were grouped into the tolerance (T), moderately tolerance (MT) and susceptible (S) categories, respectively. There was only one genotype, GU 19-68, with zero incidence of INB. Similarly, all the clones were severely infested by INB and the incidence ranged from 65 to 100% under drought conditions. The genotypes GU 19-45, GU 19-46, GU 19-61 and GU 19-55 were showed > 50% INB incidence and <6% INB intensity.
(v)Screening for multiple pest resistance in exotic clones of sugarcane
From the germplasm collection at Sugarcane Breeding Institute Research Centre, Kannur 600 exotic clones were taken up for screening against major pests of sugarcane in different hot spots. The screening was taken up at Motipur, Sakthi Sugars Ltd, Apakudal , Sugarcane Breeding Institute Regional Centre, Karnal and Sugarcane Breeding Institute, Coimbatore for top borer, early shoot borer and internode borer , Stalk borer and White grubs respectively. Total number of exotic clones screened for different pests and number of resistant sources is given below in the table
Table. Resistance in exotic clones screened for multiple pests
S.No | Pest | No. Of Clones Screened | Resistant/Tolerant Clones Identified |
1 | Early shoot borer | 338 | 23 |
2 | Internode borer | 338 | 14 |
3 | Top borer | 260 | 18 |
4 | Stalk Borer | 242 | 0 |
5 | White grubs | 358 | 16 |
- Sixteen clones viz., TUC-472, Q-61, B34-39, CB44-105, CL41-114, CL47-143, CP29-320, CP31-394, CP33-409, CP43-33, CP50-61, PR-1049, F3, F118, F134 and LF65-3716 were found tolerant to white grubs
- Eighteen clones viz., B 34-12, B 38-192, B 39-246, B 40-270, B 43-289, B 44-130, B 51-116, CP 29-116, CP 63-326, KM 724, LF 65-3705, LF 65-4701, LF 74-1444, P 72-4, PR 1000, PR 1095, Q 2O STR, Q 27, were found to be highly resistant to top borer.
- Twenty three clones viz., B 39-250, B 41-248, B 44-130, B 45-181, CP 29-116 , CP 33-409, CP 33-425 , CP 43-47 , CP 61-43, F 49-11, F 31-450, FP 172 , H 44-2772, KN 86, KT 367 , KT 501, LF 65-4233, MOL 894 , POJ 1499, Q 50, TUC-472 , US 49-7 and 56-67 were found resistant to early shoot borer
- Fourteen clones viz., BN 134, H 51-9002, KO 201, KM 724, LF 63-911, LF 64-1988, LF 64-2815, LF 65-3662, LF 65-4233, MANA, P 72-4, POJ 1228, PR 1028 and SP 83-5073 were identified as resistant to internode borer.
(vi) Identification of genetic stock resistant for internode borer:
Indian hybrids
- The genotype “Co 293” belonging to Indian hybrids has been identified and documented as resistant to internode borer.
Saccharum robustum
- Twenty-eight genetic stocks viz., “28 NG 289,57 NG 231,57 NG 54, IJ 76-337, IJ 76-360, IJ 76-426, IJ 76-427, IJ 76-435, IJ 76-440, IJ 76-449, IJ 76-489, IJ 76-496, IJ 76-536, IJ 76-543, IJ 76-545, IK 76-64, IM 76-232, IM 76-255, IS 76-137, MOL 5698, NG 77-122, NG 77-170, NG 77-23, NG 77-24, NG 77-38, NG 77-54, NG 77-59, NG 77-79” belonging to Saccharum robustum germplasm collection has been identified and documented as field resistant to internode borer.
Saccharum sinense
- The genotype “KHADYA” belonging to Saccharum sinense has been identified and documented as field resistant to internode borer.
(vii) Identification of genetic stock resistant for pink borer:
Saccharum robustum
- Thirty-one genetic stocks viz., “57 NG 208, 57 NG 231, IJ 76-280, IK 76-64, IM 76-232, IS 76-121, NG 77-1, NG 77-13, NG 77-94, NG 77-159, NG 77-176, NG 77-213, NG 77-219, NG 77-238, IS 76-119, NG 77-58, NG 77-214, NG 77-21, IM 76-258, NG 77-24, NG 77-186, NG 77-35, NG 77-122, NG 77-57, IJ 76-497, IJ 76-375, IS 76-137, IM 76-256, 57 NG 202, IM 76-260, IK 76-100” has been identified and documented as field resistant.
Saccharum barberi
- Twenty genetic stocks viz., “Dark Pindaria, DhaurAlig., Kansar, Kewali-14G, Mankia, Mungo-254, Nargori, Pathri, Mungo-237, Mungo-252, Khari, Pararia-257, Matanwar, Dhaur Kinara, Chin, Baroukha, Khatuia-124, Manga(sic), Kewali, Maneria Imp-1552” belonging to Saccharum barberi germplasm collection has been identified and documented as field resistant.
Saccharum sinense
- Eight genetic stocks viz., “Agaul, Kheli, Malani, Khadya, Maneria Imp-1648, Khakai, Lalkhadi, Ikhri” belonging to Saccharum sinense germplasm collection has been identified and documented as field resistant.
(viii) Identification of genetic stock resistant for scale insects:
- Sixty-one genetic stocks belonging to Saccharum spontaneum germplasm collection has been identified and documented as field resistant. The accessions SH 61-4-1 and SH 61-4-3 were totally free infestation.
(ix) Identification of genetic stock resistant for leaf mite:
Three genetic stocks, viz. IS 76–164, IS 76–173 and IS 76–151 have been identified moderately resistant to the exotic mite from the ISSCT collection of Saccharum spontaneum germplasm.
Insect Toxicology
- Analytical methods were developed to determine the residues of insecticides in different matrices of sugarcane crop ecosystem employing HPLC and GC with appropriate detectors. A rapid and sensitive analytical method for simultaneous determination of imidacloprid and thiamethoxam residues in the soils of sugarcane ecosystem by reversed-phase HPLC was developed with the limit of quantification of the method was 0.01 μg/g.
- Rapid analytical method to study the dissipation kinetics of chlorantraniliprole in soil of sugarcane ecosystem was standardised
- The persistence and dissipation kinetics of clothianidin in the soil of tropical sugarcane ecosystem was studied. Half-life of clothianidin was 17.2 and 17.4 days at the single and double doses, respectively. Clothianidin was observed to be more persistent than imidacloprid and thiamethoxam in the soil of tropical sugarcane ecosystem
- A simple and sensitive single-step method for gas chromatography–mass spectrometric determination of fipronil and its metabolites in sugarcane juice, jaggery and sugar was also developed at Entomology section
- At the ICAR-SBI, a multiresidue method has been developed and validated for the simultaneous determination of organophosphorus insecticides and their toxic metabolites in sugarcane juice and refined sugar by gas chromatography with flame photometric detection.
- Development, validation and application of a sensitive analytical method for residue determination and dissipation of imidacloprid in sugarcane under tropical field condition
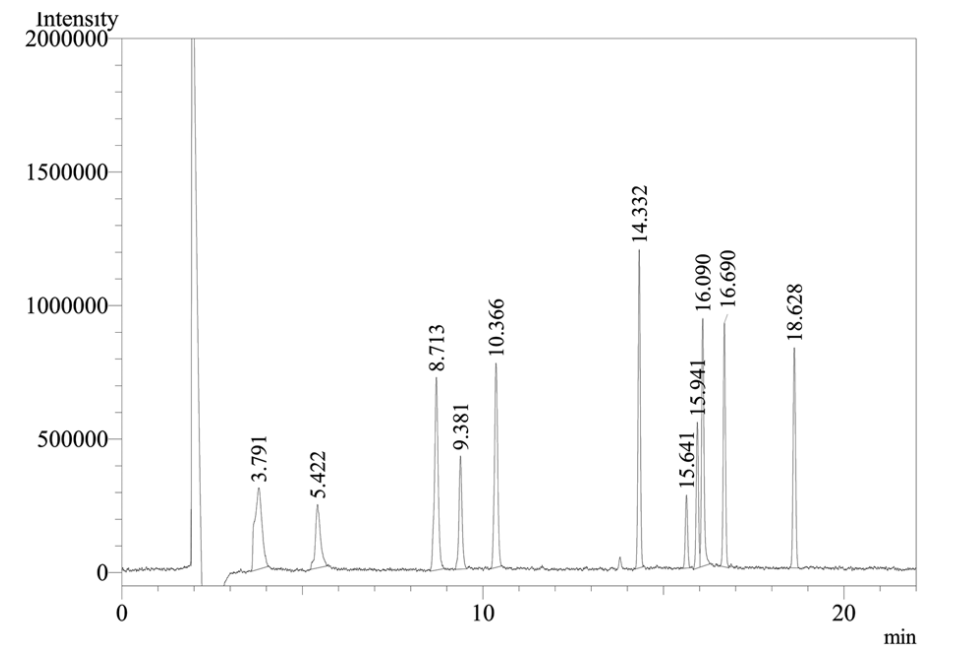
Multi-residue method for OPs and their metabolites
(Recovery chromatogram for ethyl acetate extraction and d-SPE-based cleanup with PSA)
Insect Molecular Biology
DNA barcodes for almost all insects in the sugarcane crop ecosystem. Many of the DNA barcodes developed by us are the first-ever DNA barcodes for the species concerned.

Illustrative barcode of sugarcane scale Melanaspis glomerata
(Sample I.D.: SE_CBE_SBITR of BOLD)
- The DNA barcodes were developed for the insects including, but not limited to Emmalocera depressella KX519322, Chilo infuscatellus KM453722, Chilo sacchariphagus indicus KX519326, Chilo auricilius KR153874, Scirpophaga excerptalis KJ013411, Sesamia inferens KJ013410, Melanaspis glomerata KR153875, Kritshenkella sacchari KF986271, Aleurolobus barodensis KF986269, Neomaskellia bergii KF986270, Melanaphis sacchari KM453721, Hysteroneura setariae KX519325, Tetraneura javensis KM453723, Pyrilla perpusilla KJ013412, Abdastartus atrus KX519324, Proutista moesta KX519327, Epiricania melanoleuca KX519320, Dipha aphidivora KX519319, Micromus igorotus KX519321, Sturmiopsis inferens We have also developed instar-wise transcriptome for the cane Crambids viz., early shoot borer and internode borer.
Classical studies on pest biology
Apart from the advanced studies, we have also revisited the biology of major pests of sugarcane in the recent past. These studies were performed with extraction of head-capsules of each instar of pest species involved. The number of instars in INB has recently been determined to be five as against the earlier reports of seven to eight. The ESB was observed to be pass through six instars, the FAW on sugarcane undergoes six instars to attain its pupal stage. We have also studied the detailed biology of white grub and the cane mealy bug
Head-capsules of five instars of INB
Agricultural Extension
Recent Extension and Outreach Achievements
Strengthening Technology Transfer
- The Extension Section of ICAR–Sugarcane Breeding Institute (ICAR–SBI) continued to serve as a vital bridge between research, the sugar industry, and farming communities across the country.
- A range of participatory approaches and knowledge-sharing platforms were utilised to disseminate improved sugarcane technologies, promote adoption, and obtain farmer feedback for further research refinement.
Workshops and Collaborative Programmes
- 22nd Sugarcane R&D Workshop – Southern Karnataka (20–21 June 2024, Mysuru):
ICAR- Sugarcane Breeding Institute had organized the 22nd Sugarcane Research & Development Workshop of Southern Karnataka at B.N.Bahadur Institute of Management Sciences, Manasagangothri, University of Mysore, Mysuru , during 20-21 June 2024 and discussed the following topics.
- Review of action taken on the recommendations of the previous workshop
- Managing drought & measures to improve
- irrigation water use efficiency
- Interventions for improving sugarcane yields in Southern Karnataka
- Review of mechanization initiatives in the region including mechanical harvesting
- Varietal position in sugar factories, Performance of new sugarcane varieties & AICRP (S) Varietal trials
- Sugarcane seed nursery programme
Besides discussion on these topics, an open- interactive session and a Special lecture on ‘Why should sugarcane farming be the preferred choice of farmers of Southern Karnataka?’ was delivered during the workshop. Coromandel Sugars Ltd.., Makavalli and M. Visvesvaraya Sugarcane Research Centre, Mandya of S.Nijalingappa Sugar Institute, Belagavi jointly hosted the workshop. UAS-Bangalore & S..Nijalingappa Sugar Institute , Cane Development personnel from various sugar factories, officers from the Department of Agriculture, and other Cane Development organizations in Karnataka had attended the workshop. Around 250 delegates participated.
- Workshop on Management of Crown Mealybug and Pokkah Boeng (12 November 2024, Coimbatore):
- Conducted in collaboration with the Society for Sugarcane Research & Development (SSRD).
- This workshop was organized for the benefit of sugarcane development personnel belonging to the districts of Villupuram, Cuddalore, Kallakurichi, Ariyalur, Perambalur, Namakkal, Thanjavur, Tiruchirappalli, Tiruvannamalai, Dharmapuri and Erode. Addressed emerging pest and disease challenges in these districts.
- Provided practical solutions and integrated management strategies to cane development officers and field staff.
Training and Capacity Building
- A total of 21 one-day training programmes were organised, benefiting 733 trainees.
- 121 exposure visits were arranged for students and academicians, involving 8,932 participants.
- 53 customised advisory sessions were held for 134 farmers, offering location-specific solutions.
- Major training highlights:
- TSSC – Scientific Sugarcane Cultivation (Miraj Taluk, Maharashtra, Feb 2024)
- TISP-24: Improving Sugarcane Productivity (Andhra Pradesh, March 2024)
- TSP-24: Sugarcane Production (Palus Taluk, Maharashtra, Dec 2024)
- The training programmes aimed at improving farm-level practices, productivity, and varietal adoption across multiple states.
Capacity Building Programmes at ICAR-SBI
S.No. | Month (2024) | One-day Trainings | Exposure Visits | Personal,CustomizedAdvisories | States | ||||
No. | Participants | Number of visits | Participants | Number | Participants | ||||
1 | January | 4 | 144 | 14 | 1346 | 3 | 8 | TN, Maharashtra, Telangana, Puducherry & Kerala | |
2 | February | 3 | 68 | 19 | 1408 | 9 | 18 | TN, Kerala, Karnataka, Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh & Andhra Pradesh | |
3 | March | – | – | 11 | 739 | 9 | 16 | TN, Karnataka, Maharashtra, Meghalaya, Himachal Pradesh & Bihar | |
4 | April | 2 | 32 | 15 | 1204 | 3 | 6 | TN, Maharashtra, Karnataka & Uttar Pradesh | |
5 | May | 1 | 52 | 4 | 272 | 4 | 29 | TN, Maharashtra & Karnataka | |
6 | June | – | – | 3 | 160 | 3 | 13 | TN, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka & Kerala | |
7 | July | 2 | 91 | 6 | 460 | 5 | 13 | TN, Maharashtra & Kerala | |
8 | August | 2 | 73 | 5 | 612 | 6 | 9 | TN, Maharashtra & Puducherry | |
9 | September | 2 | 82 | 13 | 758 | 6 | 9 | TN, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka & Maharashtra | |
10 | October | – | – | 12 | 827 | 3 | 6 | TN & Maharashtra | |
11 | November | 3 | 107 | 7 | 281 | 1 | 6 | TN, Kerala & Karnataka | |
12 | December | 2 | 84 | 12 | 865 | 1 | 1 | TN, Maharasthra, Kerala & Uttar Pradesh | |
TOTAL | 21 | 733 | 121 | 8932 | 53 | 134 | |||
Frontline Demonstrations and Field Days
- Two Frontline Demonstrations (FLDs) were conducted on newly released sugarcane varieties Co 11015 and Co 14012, each on one-hectare plots following recommended practices.
- Co 11015: The FLD on Co 11015 was conducted in the field of Shri. D.Gnanasekaran, S/o. Shri Dhanavel (a registered cane grower of Rajshree Sugars; DoP: 21.01.2024), Rajanthangal village, Kilpennathur Taluk, Tiruvannamalai Dt.
- Co 14012: The FLD on Co 14012 was conducted in the field of Shri. T.Thirukumaran. S/o. Shri Thangavel, Mathur village, Anthiyur Taluk, Erode district (a registered cane grower of Sakthi Sugars Ltd.; DoP: 11.01.2024).
- Farmers were provided with planting materials and incentives.
- Field Day Events:
- Field Day for Co 11015 (28 June 2024) and for Co 14012 (17 December 2024) attracted large farmer participation and showcased varietal performance and management practices. During the event, the farmers and development personnel were taken around the Frontline Demonstration (FLD) plots
Visits and Collaborations
- The Institute team visited ‘Cane-ovator’ award-winning farmer Shri Anthonysamy’s field in Tenkasi district, where the Co 86032 variety yielded 200 tonnes/ha in its 30th ratoon—an exemplary instance of sustainable productivity.
- Technology Park:
- Established with 17 sugarcane varieties and tissue culture plants for demonstration and seed production.
- Served as a live repository of varietal diversity and technological innovation.
- Collaboration with Krishi Vigyan Kendras (KVKs):
- Active participation in KVK events in Dharmapuri and Erode districts.
- Provided expert suggestions for enhancing sugarcane farmers’ income through better agronomic and mechanisation practices.
Participation in Exhibitions and Public Events
- Agri-Intex 2024, Coimbatore (11–15 July 2024):
- ICAR–SBI showcased innovations and interacted with a diverse audience of farmers, entrepreneurs, and students.
- State-Level Mega Farmers’ Day 2024 (TNAU, Coimbatore, 26–29 September 2024):
- The Institute received the ‘Best Stall Award’ for its interactive exhibits on sugarcane technologies.
- National Science Day (28 February 2024):
- Celebrated under the theme “Indigenous Technologies for Viksit Bharat.”
- School and college students visited research facilities, including biotechnology labs, the museum, and the agribusiness incubator.
Publications and Knowledge Dissemination
- The Extension Section compiled and published key institutional outputs:
- ICAR–SBI Annual Report 2023
- ICAR–SBI News quarterly issues (January, April, September, and December 2023)
- These publications captured research highlights, outreach activities, and stakeholder success stories.
Media and Communication Initiatives
- Farm School on All India Radio:
- A pioneering radio-based learning series in Tamil, titled “Sugarcane Farming for Prosperity”, launched in collaboration with Akashvani, Coimbatore.
- 119 farmers enrolled, with 13 broadcast sessions covering topics such as varietal selection, agronomy, irrigation, mechanisation, and entrepreneurship.
Farm School on All India Radio
Topics and Resource Persons | Date of broadcast |
1 Sugarcane Production – an overview’ by Dr.G.Hemaprabha (Interview mode) | 24.7.24 |
2 Promising Varieties for Tamil Nadu by Dr P.Govindaraj | 31.7.24 |
3 Micropropagation in sugarcane by Dr. D.Neelamathi | 07.08.24 |
4 Quality seed production in Sugarcane by Dr. A.Annadurai | 21.08.24 |
5 Cane agronomy by Dr.K.Kannan | 28.08.24 |
6 Irrigation and ratoon management in sugarcane by Dr.P.Geetha | 04.09.24 |
7 Nutrient Management in sugarcane by Dr.C.Palaniswami | 11.09.24 |
8 Mechanization in sugarcane by Dr T. Arumuganathan | 18.09.24 |
9 Value added products from Sugarcane by Dr. K. Hari | 25.09.24 |
10 Integrated Disease management in sugarcane by Dr. A. Ramesh Sundar (Interview mode) | 02.10.24 |
11 Integrated Pest Management in Sugarcane by Dr. B. Singaravelu | 09.10.24 |
12 Sources of Sugarcane Information by Dr. D. Puthira Prathap | 16.10.24 |
13 Entrepreneurship development in sugarcane by Dr. P. Murali | 23.10.24 |
- Radio and Video Features:
- Several features broadcast through All India Radio (Coimbatore & Dharmapuri) on DAPSTC activities and field demonstrations.
Video features on innovations such as Soil Moisture Indicators ( https://tamil.news18.com/technology/coimbatore-sugarcane-breedinginstitute-discover-soil-moisture-indicator-forwater-saving-rkj-mkn-local18-1586209.html ) and Energy Canes (https://www.news18.com/india/this-institute-in-coimbatore-breeds-a-special-variety-of-sugarcane-for-ethanol-production-9078220.html ) aired on News18 Tamil Social Media Outreach:
- Regular updates shared through Facebook, YouTube, and X (Twitter) to engage with stakeholders nationwide ((https://www.facebook.com/icar.sbi ) , YouTube (http://www.youtube.com/@icar-sugarcanebreedinginst1942; http://www.youtube.com/caneinfo) X (@BreedingIcar).
Development Action Plan for Scheduled Tribe Component (DAPSTC)
- Implemented in Sathyamangalam Tiger Reserve (Erode district) and Chinna Kalrayan Hills (Salem district), Tamil Nadu.
- Expanded to Salem following a request from the Tamil Nadu State Rural Livelihood Mission (TNSRLM).
- Activities included:
- Needs assessment and baseline surveys in tribal settlements such as Pallikkadu, Molayanoor, Thaloor, Vilampatti, and Valoothu.
- Launch of Tribal Nutrition Awareness and Training Campaign (12 March 2024), inaugurated by the District Collector and ICAR–SBI Director.
- Awareness campaigns in multiple villages emphasising nutrition, millet cultivation, and income generation through agri-entrepreneurship.
- Distribution of farm tools, seed kits, and household items to tribal families.
- Training the Tribal Sugarcane farmers:
- Two tribal settlements viz., Molayanoor and Vilampattu have tribal farmers who had been growing sugarcane for a long time. A ‘Training Campaign for Tribal Sugarcane Farmers’ as part of project was organized at Karumanthurai, Chinna kalrayan hills, Salem district 27 June 2024 for the tribal sugarcane farmers of Molayanoor and Vilampattu. The Director of ICAR- Sugarcane Breeding Institute, Managing Director of Subramaniya Siva Co-op Sugars, officials from TNSRLM and several tribals participated in the programme. A publication entitled ‘Sugarcane varieties suitable for Tamil Nadu/ was published as part of DAPSTC project.
- Tribal awareness cum training campaigns
- As part of DAPSTC project, ‘Tribal Nutrition Awareness cum Training’ Campaigns were conducted in Ittarai and Thadasalatti villages. During these campaigns, sessions for knowledge empowerment were handled by experts and farm tools, household items, seed kits for setting up nutrition garden, radio sets, areca nut seedlings, vermicompost, liquid jaggery etc., were distributed among all the tribal households. All tribals who participated in these campaigns were administered the ‘Pledge against malnutrition’. Extension literature on setting up of nutrition gardens, millet cultivation, leaflet on All India Radio programmes, Fall Army Worm Management, Arecanut cultivation and Millet recipes were prepared and distributed. Pulverizers along with logbooks were handed over to the tribal hamlets.
- Empowerment of indigenous communities through millet-entrepreneurship was highlighted during the conduct of ‘Tribal awareness cum training campaign’ among the tribals in Pallikkadu tribal settlement in Aladipatti panchayat of Salem district on 29 August 2024. The campaign was conducted as part of STC project being implemented by the Institute, in collaboration with Tamil Nadu State Rural Livelihood Mission (TNSRLM), Salem. Scientists from ICAR-SBI, ICAR-CIAE, TANUVAS and TNAU handled the training sessions.
- The significance of growing vegetables and milletsand including them in the daily diet of indigenous communities was highlighted during the conduct of ‘Tribal awareness cum campaign’ among the tribals in Thaloor and Valoothu tribal settlements in Aladipatti panchayat of Salem district on 13 August 2024. Scientists from ICAR-SBI, ICAR-CSWRI and TNAU handled the training sessions.
- Impact Evaluation:
- Surveys and media coverage confirmed improvements in nutrition, livelihoods, and awareness.
- Evaluations conducted by ICAR ( Global AgriSystem Pvt. Ltd.,) with features published in Dinamalar ( https://www.dinamalar.com/news/premium-news/mountain-residence-without-electricity–pudupolivu-now-by-central-government-scheme-/3739671 ); (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mmEtodjI_mo); and News18 Tamil (https://tamil.news18.com/coimbatore/sugarcane-breeding-instituteproviding-basic-needs-to-malasar-tribe-peopleliving-in-forest-rkj-mkn-local18-1619382.html )
Impact Studies and Research-based Assessments
- Evaluation of State-Level R&D Workshops:
- A cross-state assessment conducted in Southern Karnataka with 82 respondents.
- Key findings:
- Strong networking and expert interaction motivated participation.
- Topics on varietal improvement and crop protection were most valued.
- High satisfaction reported regarding resource persons, content clarity, and opportunities for discussion.
- Tangible impacts observed on varietal use, eco-friendly farming, and micro-irrigation adoption.
- Social Impact Assessment of Micropropagation in Sugarcane:
- Survey among 41 cane staff revealed that micropropagated plants from ICAR–SBI and private labs were highly preferred for quality and genetic purity.
- Benefits: high yield potential, faster varietal multiplication, and uniform crop stands.
- Constraints: limited availability, higher cost, and need for skilled manpower.
- Farmer case studies confirmed success with settling nurseries and wide-row cultivation practices.
Digital Innovations
- Development of Cane Adviser App (Version 2.0):
- Work initiated to upgrade the mobile application for better interactivity and user engagement.
- The updated version aims to serve as an integrated digital advisory and networking platform for stakeholders.
Overall Impact
- Through its comprehensive extension initiatives, ICAR–SBI effectively connected laboratory research with field realities.
- The Section demonstrated leadership in technology transfer, farmer training, and inclusive rural development.
- Its efforts not only improved sugarcane productivity but also empowered farmers and tribal communities through sustained knowledge exchange and innovation.
Statistics and Economics
Recent Statistics and Economics Outreach Achievements
The Statistics and Economics Section of the institute is actively integrating modern statistical and computational tools to strengthen sugarcane research. Recognizing that robust statistical methodologies are vital for high-quality agricultural science, Statistics and Economics Section of ICAR-SBI has also initiated capacity-building programs to train researchers in advanced statistical techniques, data analysis workflows, and emerging computational approaches. These efforts aim to enhance research precision, improve decision-making, and promote data-driven advancements in sugarcane improvement and productivity.
Statistical packages developed for efficient crop data analysis
- The R package “CANE: Comprehensive Groups of Experiments Analysis for Numerous Environments” designed for multi-spatial and multi-temporal data analysis. It is especially valuable in agricultural research where treatment × location and treatment × season interactions must be considered to ensure valid conclusions across diverse environments. DOI: https://doi.org/10.32614/CRAN.package.CANE.
- The R package “PhysioIndexR: Physiological and Stress Indices for Crop Evaluation” provides a unified framework for computing key physiological traits, stress indices, and derived metrics essential for crop improvement and stress resilience studies. By integrating physiology-based traits with stress indices, PhysioIndexR enables the identification of multi-stress-resilient and superior genotypes, supporting genetic advance & sustainable production of food, fuel, & fibre under climate change & resource limitations. DOI: https://doi.org/10.32614/CRAN.package.PhysioIndexR.
Training and Capacity Building
- Successfully organized a four-day hands-on training programme on “Comprehensive Training on Biological Data Analysis Using R” at ICAR-SBI, Coimbatore, from 20–23 May 2025. A total of 24 participants, including students and faculty, attended the programme. The training covered eight sessions on statistical data analysis in R, including data visualization, design of experiments, hypothesis testing, multivariate analysis, and genetic diversity analysis. The programme also introduced methodological frameworks for policy and technology evaluation, such as decomposition of technology impact, qualitative response regression models, and time series analysis in agricultural research.
Outputs of the Scientific Trainings:
- The book “Basic and Applied R Programming for Agricultural Research” contains twelve chapters focused on data visualization and design of experiments, helping readers build strong skills in graphical analysis, experimental planning, and data interpretation. It further strengthens analytical capabilities through chapters on hypothesis testing and multivariate analysis, while specialized sections such as genetic diversity analysis highlight R’s interdisciplinary relevance in agricultural sciences. The book also covers methodological frameworks for policy and technology evaluation, including decomposition of technology impact, qualitative response regression models, and time series analysis in agricultural research. ISBN: 978-93-85267-46-8.